Topic 1: Cell biology 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about cell biology.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Cell biology revision resources
This page lists the understandings and skills expected for Topic 1 and links to the sub-topic pages which contain detailed revision notes, activities and past paper style questions. Great for revision.
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
The four cells shown below have each been surrounded by a solution for 1 hour.
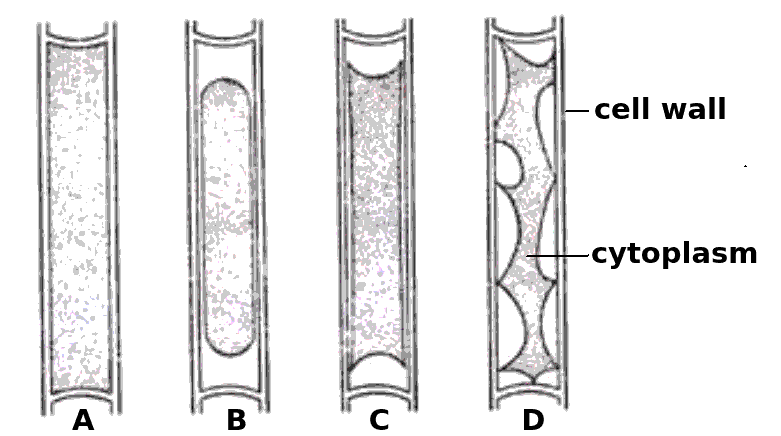
Which cells have been in a hypertonic solution ?
Cell A is swollen turgid, it is in a hypotonic solution or an isotonic solution.
The cells B, C and D show increasing signs of plasmolysis, and so they must be in hypertonic solutions.
Skill: Estimation of osmolarity in tissues by bathing samples in hypotonic and hypertonic solutions. (Practical 2)
The electron microscope image below shows a ciliated epithelial cell from the trachea.
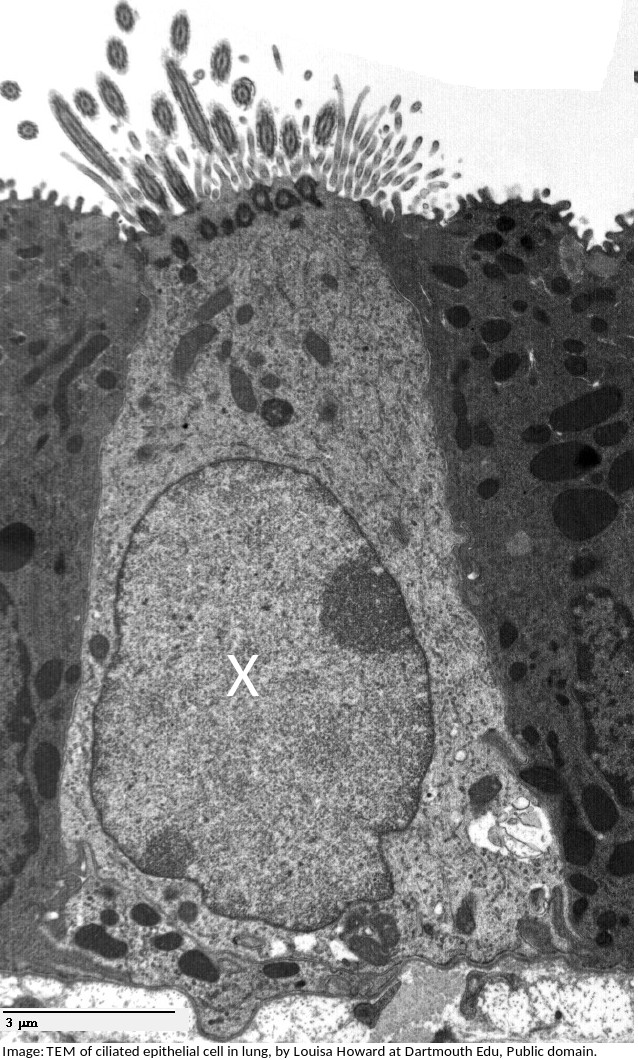
What is the name of the organelle labelled X?
Explain the significance of the following terms in Biology; Metabolism, response, growth, reproduction, excretion, nutrition, homeostasis.
Remember MR H GREN. These letters represent the seven characteristics of living things.
Stargarts disease, which causes loss of cells in the retina can be treated using a special type of human cell.
Which of the following is used because it is still able to differentiate?
Stem cells can differentiate and become specialised cells.
They often take on the features of the cells around them.
Rod cells, cone cells, and erythrocytes are specialised cells and cannot differentiate.
Which label in the image below shows the process of endocytosis?
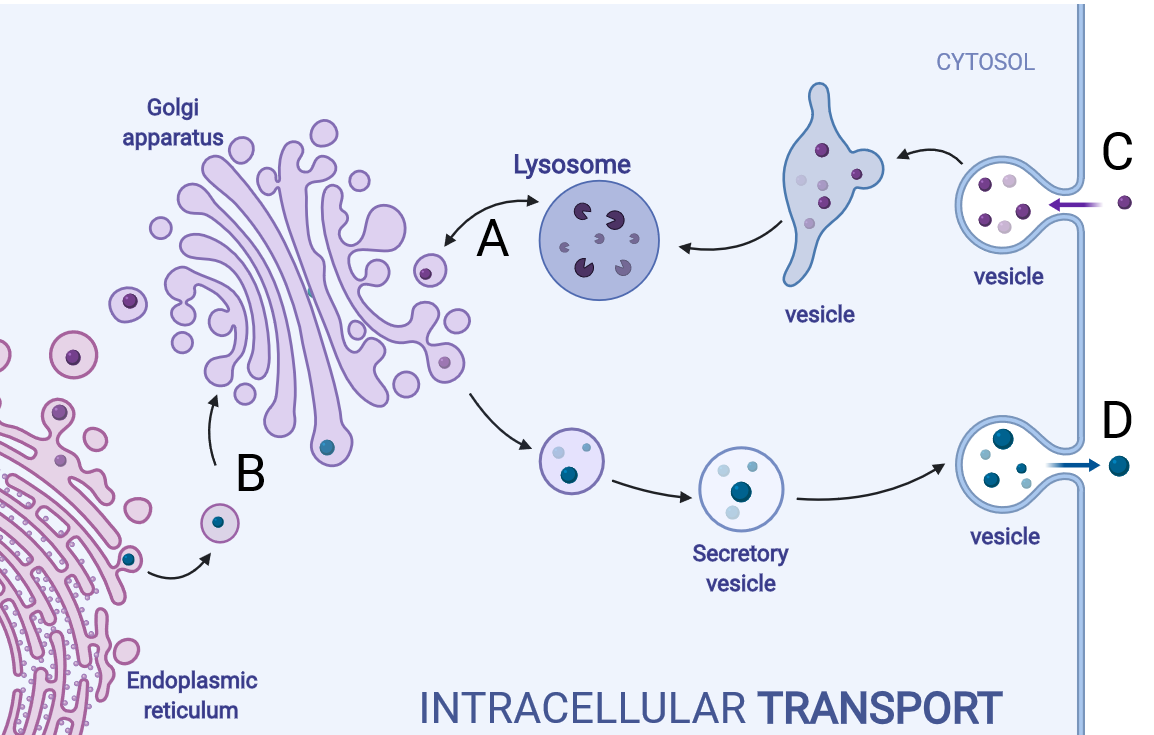
Endocytosis is the process where a substance is surrounded by the plasma membrane which forms a vesicle inside the cell that then moves into the cytoplasm, separating from the plasma membrane.
The diameter of this field of view under a microscope at X400 magnification is 250 μm.
The image below shows Dracaena leaf upper epidermis cells.
Which is the best estimate of the width (from left to right) of an epidermal cell?
Comment: There are approximately 8 cells across a diameter so 250/8 = 33 μm.
Beware of the units, mm are 1000 times bigger than µm.
Why is a fungal hypha an exception to the cell theory?

A fungal hypha has many nuclei in a hypha but no cross walls to divide the hypha into cells.
What is the approximate length of the bacterial cell in the image?

The scale bar is 1 µm and the bacterium is approximately 3 times the length of the scale bar.
The diagram shows a typical eukaryotic plant cell. Which organelles are involved in supporting the cell and plant? I Cell wall II Cytoplasm III Nucleus IV Vacuole.

The cell and plant are supported by the turgor pressure of water in the vacuole acting on the rigid cell wall.
The image is of a prokaryotic cell. Which feature defines the cell as prokaryotic?

The lack of a membrane bound nucleus (nucleoid) classifies a cell as prokaryotic.
Protein channels cross the membrane to allow hydrophilic substances to pass through the membrane.
The diagram is of a plasma membrane. Which label corresponds to the hydrophilic area of an amphipathic molecule?

Protein (5) has both hydrophilic and hydrophobic areas to act as an integral protein. The central channel is hydrophilic.
The microphotograph is of stratified epithelium. Cells are produced by mitosis in the area marked 1 and eventually reach the surface to replace lost cells. Which biological processes does this represent?

The cells produced by mitosis differentiate into mature cells and replace the cells lost at the surface.
Which means of transport across a plasma membrane requires the molecule shown in the picture?

Which process is involved in white blood cells engulfing bacteria (arrowed in the photomicrograph)?

White blood cells engulf bacteria by endocytosis, the intake of solid particles by a cell membrane.
Which is the best description of the genetic code?
The genetic code is universal (the codons code for the same amino acid in all organisms) but there are a very few exceptions, mostly in Archaea. A mutation does not alter the genetic code, it alters the base sequence of DNA.
The theory of spontaneous generation has been disproved by Pasteur's experiment. Is there a point in evolution when spontaneous generation did occur?
The first cells must have arisen spontaneously from non-living matter, probably in volcanic vents, but the universal nature of cell ultrastructure and of the genetic code makes it likely that this only happened once.
Which component of the plasma membrane varies in function between differentiated cells?
The protein component of the membrane varies in structure and function.
How do integral proteins remain within the phospholipid bilayer?
Integral proteins have a hydrophobic centre that associates with the fatty acid inner layer of the bilayer and a hydrophilic head that associates with the phospholipid heads.
Why is the cell component in the image regarded as an organelle?

The organelle is a cell component with a membane, the mitochondrion, it is adapted to aerobic respiration.
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.


 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn