Topic 1: Cell biology 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about cell biology.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Cell biology revision resources
This page lists the understandings and skills expected for Topic 1 and links to the sub-topic pages which contain detailed revision notes, activities and past paper style questions. Great for revision.
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
Cells today come from pre-existing cells. The origin of the fist cell must be different.
Where do biologists think the first cell came from?
The first cell must have come from non-living material. This material must have contained molecules which today we consider as organic, carbon containing molecules.
The electron microscope image below shows a ciliated epithelial cell from the trachea.
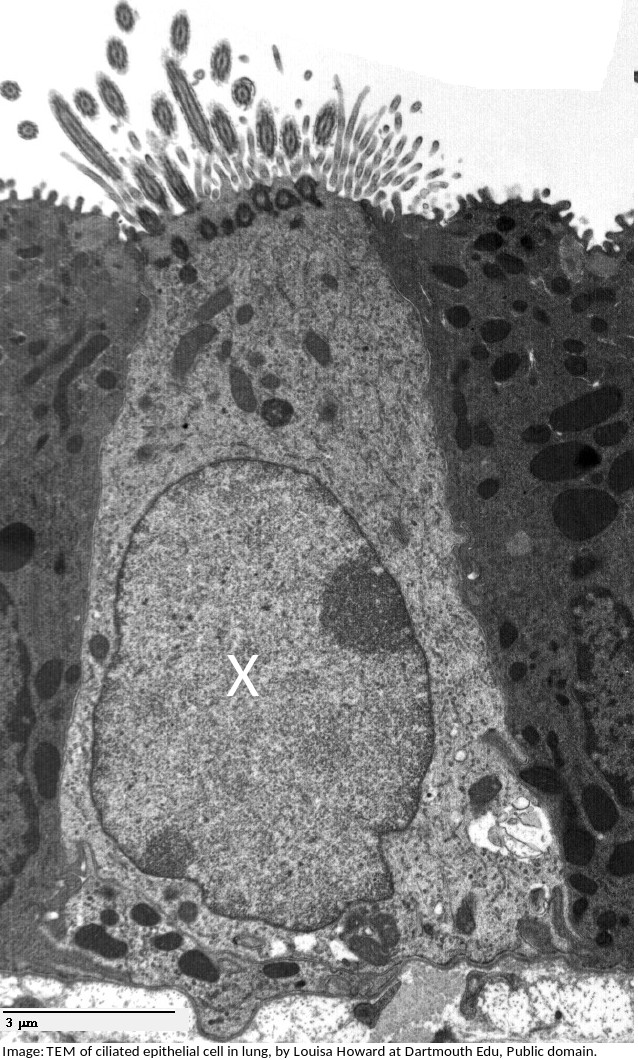
What is the name of the organelle labelled X?
What are the structures labelled X and Y likely to be in this electron microscope image?
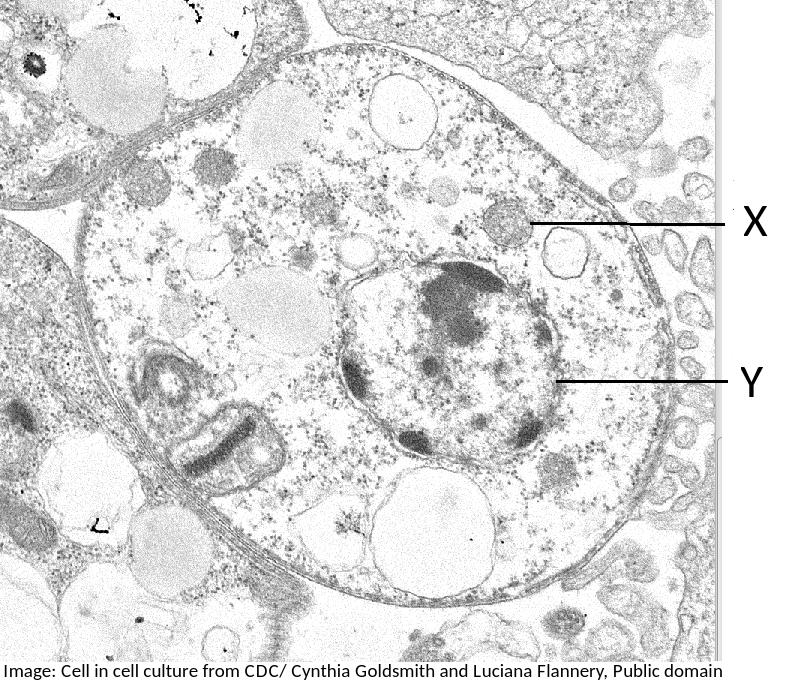
Students are expected to be able to identify organelles from microscope images of cells. The nucleus is distinctive because it is about 10µm in size, and it has black dots in it, chromatin, and sometimes one or more dark patches within the nuclear membrane. It also has a double membrane, not often easily visible.
This electron microscope image shows a group of prokaryotes.
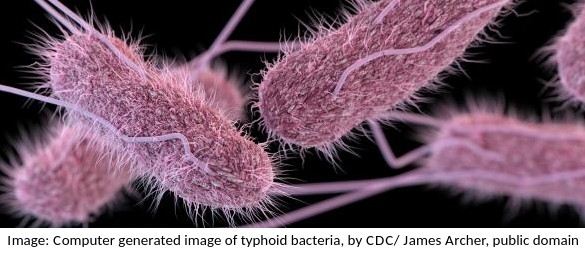
What structures are most likely to be found inside these cells?
Skill: you should know how to draw prokaryotic cells (with a cell wall, plasma membrane, cytoplasm, pili, flagella, 70s ribosomes and nucleoid.) and eukaryotic cells (free 80s ribosomes, rough endoplasmic reticulum (rER), lysosome, Golgi apparatus, mitochondrion and nucleus)
What is the term used to describe the smallest distance which two objects can be seen as separate objects in a microscope?
The resolving power, or resolution, is the ability to separate objects, to produce separate images of two objects.
Explain the significance of the following terms in Biology; Metabolism, response, growth, reproduction, excretion, nutrition, homeostasis.
Remember MR H GREN. These letters represent the seven characteristics of living things.
Which of the structures listed below are involved in membrane transport?
Many transmembrane proteins are involved in transport of molecules across membranes. These can either provide a sort of molecular pore through which ions or molecules can pass (facilitated diffusion), or they can use ATP to actively move molecules, even against the concentration gradient (active transport).These are just two examples, transport can also occur by simple diffusion through the phospholipid bilayer, or by endocytosis.
Which phrases most accurately describe a multicellular organism?
Comment: The multicellular condition allows for differentiation into cells of different types and also replacement of cells when injured or damaged.
The diameter of this field of view under a microscope at X400 magnification is 250 μm.
The image below shows Dracaena leaf upper epidermis cells.
Which is the best estimate of the width (from left to right) of an epidermal cell?
Comment: There are approximately 8 cells across a diameter so 250/8 = 33 μm.
Beware of the units, mm are 1000 times bigger than µm.
Which of the following are methods by which molecules can move across membranes?
I. Simple diffusion
II. Facilitated diffusion
III. Cytokinesis
IV. Active transport
There are actually four types of membrane transport which are required in DP Biology, Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis and active transport.
Which organelle is visible in an electron microscope but not in a light microscope?

The ribosome is too small to be seen in the electron microscope, the other organelles were seen in the light microscope before the electron microscope was invented.
Which organelles are found in large numbers in secretory cells in animals? I Vesicles II Golgi Body III Mitochondria IV Rough endoplasmic reticulum.

Secretory cells synthesise proteins for exocytosis so have large numbers of mitochondria to supply energy, RER to synthesise the proteins for packaging into vesicles by the Golgi Body.
The image shows a transverse section of a plant cell seen using an electron microscope.
What is the main function of the large organelle (A) seen in the cell?

The organelle shown is the nucleus, it stores the genetic information, DNA and is the location of DNA replication and Transcription.
The image is of a channel protein. What is the function of a membrane channel protein?

Channel proteins are used for facilitated diffusion down the concentration gradient.
Which is the best description of the genetic code?
The genetic code is universal (the codons code for the same amino acid in all organisms) but there are a very few exceptions, mostly in Archaea. A mutation does not alter the genetic code, it alters the base sequence of DNA.
Which property of stem cells is important for embryonic development?
Stem cells can divide and differentiate along different pathways. For a single fertilised egg cell to grow into an embryo both these processes are necessary.
All eukaryote cells have differing combinations of the same types of organelles. How can this be explained?
Similarity in structure and function are taken as evidence of a common ancestor. All of the other statements are partially true but do not provide an explanation.
In which ways is a plasma membrane fluid?
I The shape is flexible
II Proteins can move in and out of the membrane
III Proteins can move within the membrane
IV It can reseal a small puncture.
The membrane can reseal if slightly damaged and the shape is flexible. Proteins cannot move in and out of the membrane but can move within the membrane.
Which component of the plasma membrane varies in function between differentiated cells?
The protein component of the membrane varies in structure and function.
The image below was taken in 1825 and shows part of the cell cycle.
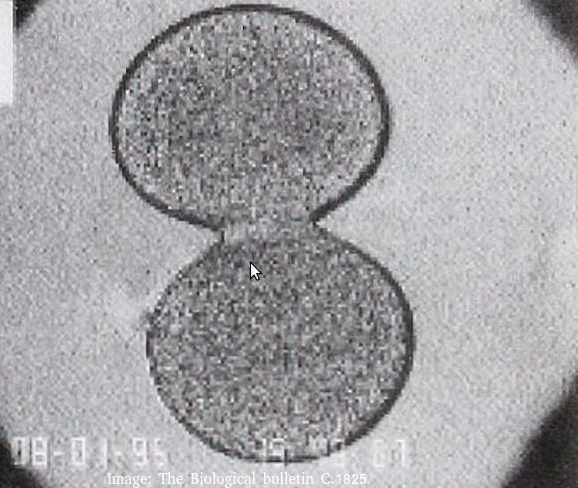
What is shown in the image?
Cytokinesis occurs after mitosis in plant and animal cells.
Animal cells form a cleavage furrow (looks like a wasps waist) as they don't have cell walls.
The two daughter cells are the same size, so cytokinesis is equal.
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.

 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn