Topic 1: Cell biology 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about cell biology.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Cell biology revision resources
This page lists the understandings and skills expected for Topic 1 and links to the sub-topic pages which contain detailed revision notes, activities and past paper style questions. Great for revision.
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
The image below shows a eukaryotic cell.
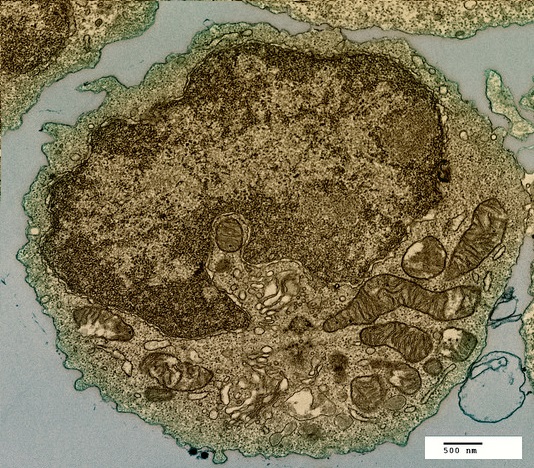
Which structure, visible in the image, could be used as evidence supporting endosymbiosis?
The mitochondria provide evidence supporting endosymbiosis because they have:
- a double membrane
- 70S ribosomes
- DNA
The image below shows two cells undergoing mitosis.
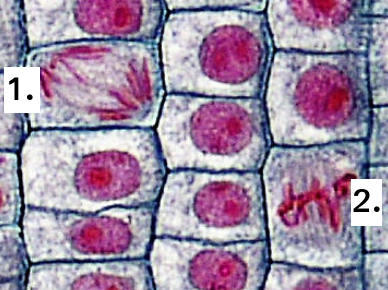
Which of the following correctly identifies the stage of mitosis for each of the cells?
Identification of the phase of mitosis is an important skill.
The position of the chromosomes gives the best clue.
In Prophase, they are spread around the cell, and double stranded.
In Metaphase, the chromosomes are lined up on the spindle equator.
In Anaphase, the chromosomes are moving to opposite poles of the cell.
In Telophase, the two groups of chromosomes are separate, sometimes with a nuclear membrane.
The illustration shown below is of a protein (green) attached to a membrane.
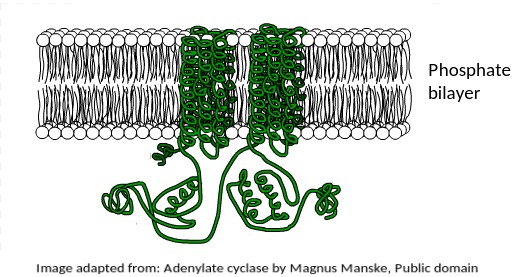
What is the most likely function of this membrane protein?
This protein is found in the human liver, where the hormone adrenaline indirectly stimulates it to mobilise stored energy inside liver cells in the "fight or flight" response.
The fact that it is a transmembrane protein is essential for this function.
It is interesting to note that this protein is also secreted by Anthrax bacteria as a toxin.
It upsets the metabolism of host cells when it enters them.
The electron microscope image below shows three organelles found in an animal cell.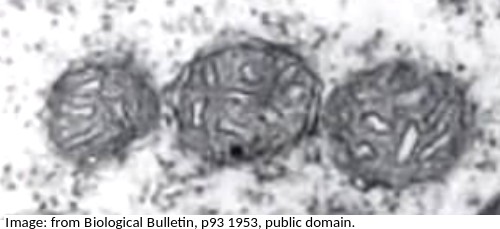
What is the name of the organelles?
Know how to idenfity the organelles in eukaryotes and draw their compartmentalised structure.
A mitochondrion (pleural = mitochondria) has an outer membrane and inner membrane folded into long thing 'flaps' called cristae.
The electron microscope image below shows an organelle found in both animal and plant cells.

What is the name of the organelle?
Know how to idenfity the organelles in eukaryotes and draw their compartmentalised structure.
The rER has parallel membranes covered in dots, which are ribosomes, used for making proteins, for secretion from the cell.
The electron microscope image below shows a ciliated epithelial cell from the trachea.
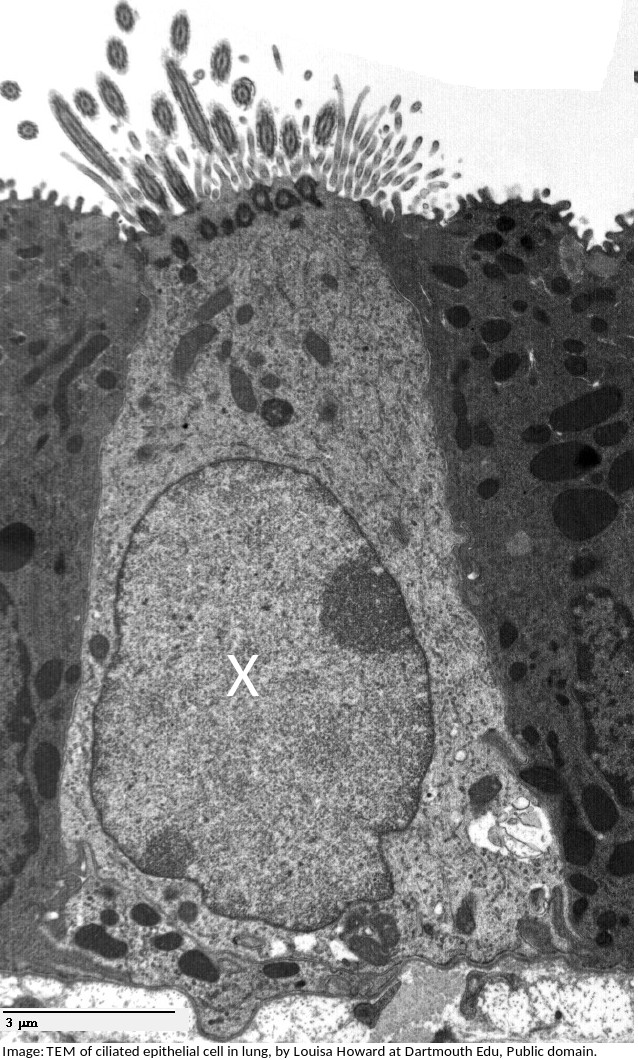
What is the name of the organelle labelled X?
What is the importance of surface area to volume ratio to cells?
Surface area to volume ratio is important in the limitation of cell size. The lager the volume, the greater the need for materials which have to be exchanged over the surface of the cell.
Stargardts disease is vision loss caused by the death of both cone cells and rod cells in the part of the retina around the fovea. One potential treatment for Stargardts disease is the use of human embryonic stem cells.
What are the properties of these stem cells, which other cells don't have, that makes them so useful for this treatment?
Stem cells can divide and this help researchers to grow them in the lab.
They can differentiate along different pathways in embryonic development which makes stem cells useful for therapeutic uses (e.g. Stargart's disease) because they can be grown into many different tissues.
The electron microscope image below shows a scale bar marked with 100µm.
The large 'goblet cell' in the centre is producing mucous which will protect the surface of the epithelium.
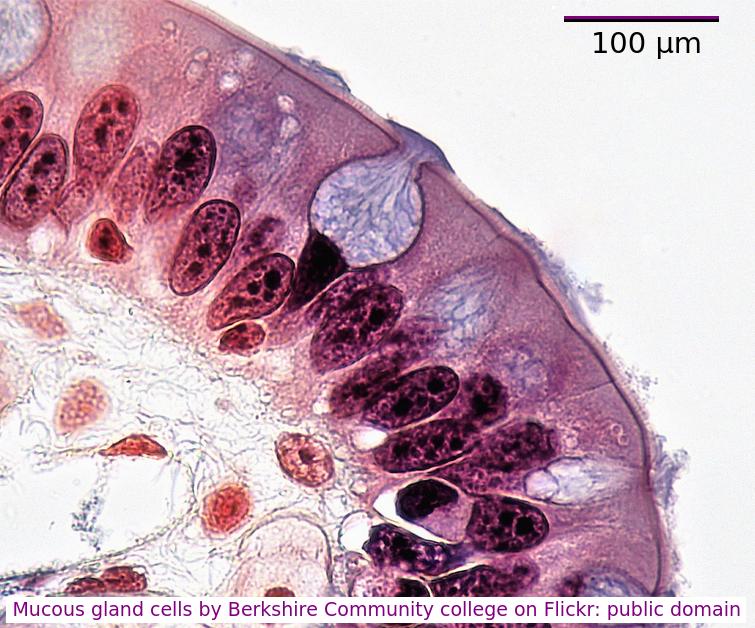
What is the diameter of the goblet cell?
Accurately, measure the scale bar length in mm, measure the diameter of the cell, in mm
divide cell diameter by scalebar and multiply by 100µm.
You can often estimate the size using the scale bar and your thumb or a pen.
Stargarts disease, which causes loss of cells in the retina can be treated using a special type of human cell.
Which of the following is used because it is still able to differentiate?
Stem cells can differentiate and become specialised cells.
They often take on the features of the cells around them.
Rod cells, cone cells, and erythrocytes are specialised cells and cannot differentiate.
Which of the following are methods by which molecules can move across membranes?
- Simple diffusion
- Facilitated diffusion
- Cytokinesis
- Active transport
There are actually four types of membrane transport which are required in DP Biology, Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis and active transport.
Which of the structures listed below are involved in membrane transport?
Many transmembrane proteins are involved in transport of molecules across membranes. These can either provide a sort of molecular pore through which ions or molecules can pass (facilitated diffusion), or they can use ATP to actively move molecules, even against the concentration gradient (active transport).These are just two examples, transport can also occur by simple diffusion through the phospholipid bilayer, or by endocytosis.
Which is the best definition of a tissue?
Comment:Tissues may have one or several cell types and one or more functions
Human red blood cells are circular and 0.6 μm in diameter. A photograph of a red blood cell is shown as an illustration in a book with a diameter of 1.2mm. What is the magnification of the diagram?
Comment: Convert 1.2 mm into μm by multiplying x 1000 = 1200 μm (so that both units are the same). Then you can see that 0.6 x 2000 = 1200. Or use the formula Magnification = Image size/true size. If the photograph is larger than the cell, the magnification could not be 0.5x which would make it smaller. Eliminate obviously incorrect answers.
The image is of a prokaryotic cell. Which feature defines the cell as prokaryotic?

The lack of a membrane bound nucleus (nucleoid) classifies a cell as prokaryotic.
The image is of a channel protein. What is the function of a membrane channel protein?

Channel proteins are used for facilitated diffusion down the concentration gradient.
What is the sequence of events that occur in a cell that is secreting a protein hormone?
1 Exocytosis
2 Vesicle formed by Golgi Body
3 Fusion of vesicle to plasma membrane
4 RER manufactures protein.
Ribosomes on the RER manufacture protein. This is packaged in vesicles by the Golgi Body and moves to the surface of the cell where the vesicle and plasma membrane fuse and exocytosis of the protein occurs.
What is the structure of the genetic material found in a mitochondrion?
Mitochondrial DNA is a single helical molecule, not associated with protein and circular in shape. The same as prokaryote nucleoid DNA.
The theory of spontaneous generation has been disproved by Pasteur's experiment. Is there a point in evolution when spontaneous generation did occur?
The first cells must have arisen spontaneously from non-living matter, probably in volcanic vents, but the universal nature of cell ultrastructure and of the genetic code makes it likely that this only happened once.
In which ways is a plasma membrane fluid?
I The shape is flexible
II Proteins can move in and out of the membrane
III Proteins can move within the membrane
IV It can reseal a small puncture.
The membrane can reseal if slightly damaged and the shape is flexible. Proteins cannot move in and out of the membrane but can move within the membrane.
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.

 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn