Topic 1: Cell biology 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about cell biology.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Cell biology revision resources
This page lists the understandings and skills expected for Topic 1 and links to the sub-topic pages which contain detailed revision notes, activities and past paper style questions. Great for revision.
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
Huntington's Disease (HD) is a brain disorder that affects a person's ability to talk, and move. HD is caused by a faulty protein. The job of the protein is to direct vesicles containing important molecules to the outside of the cell. The chemicals are released when the vesicle reaches the membrane.
What is the name given to the release of chemicals by a cell in this way?
This is a type of secretion, the vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane and its contents are released. This is called "exocytosis".
Cells today come from pre-existing cells. The origin of the fist cell must be different.
Where do biologists think the first cell came from?
The first cell must have come from non-living material. This material must have contained molecules which today we consider as organic, carbon containing molecules.
Which cells are produced when a diploid cell divides by mitosis?
Mitosis is division of the nucleus into two genetically identical daughter nuclei in eukaryote cells.
A diploid cell will produce two diploid daughter cells in one division of mitosis.
The image below was taken in 1825 and shows part of the cell cycle.
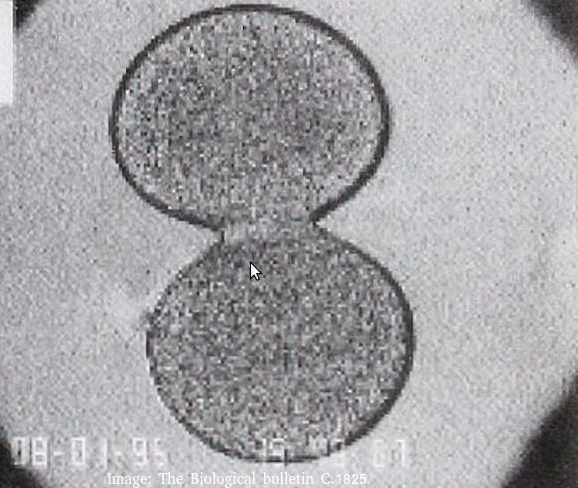
What type of cells is this and at which stage of the cell cycle?
Cytokinesis occurs after mitosis in plant and animal cells. The chromosomes are uncoiled.
Plant cells build a new cell wall which divides the cytoplasm.
Animal cells form a cleavage furrow (likes a wasps waist) as they don't have cell walls.
The image below shows two cells undergoing mitosis.
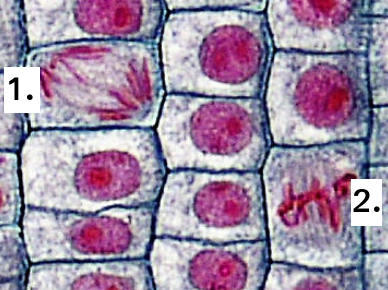
Which of the following correctly identifies the stage of mitosis for each of the cells?
Identification of the phase of mitosis is an important skill.
The position of the chromosomes gives the best clue.
In Prophase, they are spread around the cell, and double stranded.
In Metaphase, the chromosomes are lined up on the spindle equator.
In Anaphase, the chromosomes are moving to opposite poles of the cell.
In Telophase, the two groups of chromosomes are separate, sometimes with a nuclear membrane.
Which one of the statements below best describes the mitotic index?
The mitotic shows the speed of cell division, which can be used as a tool to identify cancer.
It is calculated by dividing the number of cells doing mitosis by the total number of cells.
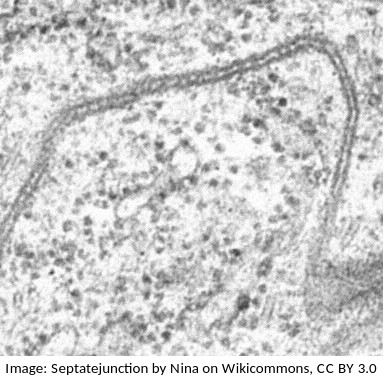 The photograph is from an electron microscope image of a membranes.
The photograph is from an electron microscope image of a membranes.
Parallel dark lines are clearly seen.
In electron micrography, heavy metal stains are often used to enhance contrast. DNA and Proteins often show as dark areas because these molecules can attach to the stain.
Which of the following interpretations is most similar to the proposal of the Daveson-Danielli model of membranes?
Students are expected to know how to use evidence from electron microscopy to support an idea about membranes. One illustration of this is the proposal of the Davson-Danielli model.
Further evidence lead to the falsification of the Davson-Danielli model and the proposal of the fluid mozaic model.
The electron microscope image below shows a ciliated epithelial cell from the trachea.
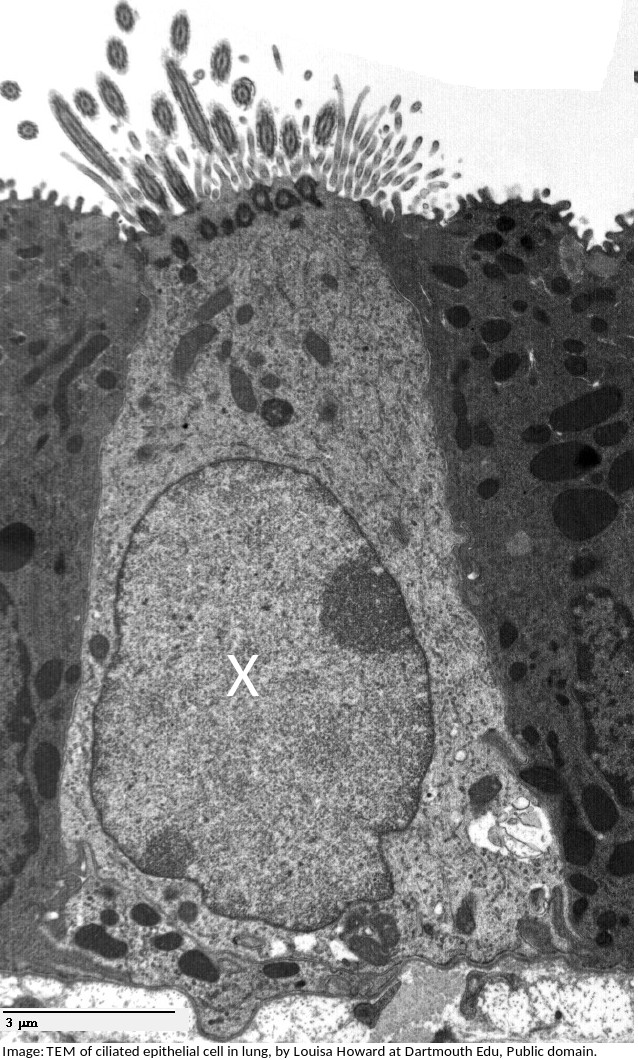
What is the name of the organelle labelled X?
What is the importance of surface area to volume ratio to cells?
Surface area to volume ratio is important in the limitation of cell size. The lager the volume, the greater the need for materials which have to be exchanged over the surface of the cell.
Which of the structures listed below are involved in membrane transport?
Many transmembrane proteins are involved in transport of molecules across membranes. These can either provide a sort of molecular pore through which ions or molecules can pass (facilitated diffusion), or they can use ATP to actively move molecules, even against the concentration gradient (active transport).These are just two examples, transport can also occur by simple diffusion through the phospholipid bilayer, or by endocytosis.
Cells are often stored in isotonic conditions because they can be damaged in other concentrations, hypertonic, or hypotonic. Which of the descriptions of hypertonic is the most accurate?
Hypertonic solutions have a higher concentration of solutes, and lower water potentials than cells.
Which phrases most accurately describe a multicellular organism?
Comment: The multicellular condition allows for differentiation into cells of different types and also replacement of cells when injured or damaged.
Which is the best definition of a tissue?
Comment:Tissues may have one or several cell types and one or more functions
Which of the following are methods by which molecules can move across membranes?
I. Simple diffusion
II. Facilitated diffusion
III. Cytokinesis
IV. Active transport
There are actually four types of membrane transport which are required in DP Biology, Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis and active transport.
Which organelle is visible in an electron microscope but not in a light microscope?

The ribosome is too small to be seen in the electron microscope, the other organelles were seen in the light microscope before the electron microscope was invented.
Which means of transport across a plasma membrane requires the molecule shown in the picture?

Which process is involved in white blood cells engulfing bacteria (arrowed in the photomicrograph)?

White blood cells engulf bacteria by endocytosis, the intake of solid particles by a cell membrane.
Which organelles in a plant cell are believed to have originated as free-living prokaryotic cells?

Both the mitochondria and the chloroplast in plant cells are thought to have been free-living prokaryotes which evolved in a symbiotic relationship with a eukaryotic cell.
What is the structure of the genetic material found in a mitochondrion?
Mitochondrial DNA is a single helical molecule, not associated with protein and circular in shape. The same as prokaryote nucleoid DNA.
All eukaryote cells have differing combinations of the same types of organelles. How can this be explained?
Similarity in structure and function are taken as evidence of a common ancestor. All of the other statements are partially true but do not provide an explanation.
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.

 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn