Topic 1: Cell biology 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about cell biology.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Cell biology revision resources
This page lists the understandings and skills expected for Topic 1 and links to the sub-topic pages which contain detailed revision notes, activities and past paper style questions. Great for revision.
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
Pasteur's experiment with 'swan neck' flasks showed that a sterile nutrient medium exposed to the air would not show any signs of bacterial growth under his conditions.
What prevented the growth of bacteria?
Pasteur's famous experiments with swan neck flasks showed that broth kept in a flask where no dust could settle in the nutrient medium, and thus no living cells could get in, would not go mouldy.
This disproved the theory of spontaeous generation.
During interphase of the cell cycle what happens to the DNA in the nucleus?
Under the microscope there is little change during interphase.
However interphase is a very active phase of the cell cycle with many processes occurring in the nucleus and cytoplasm. (It is subdivided into G1, S, G2 phases of the cell cycle)
DNA replication occurs during the S-phase.
The graph below shows the % change in mass of carrot parenchyma slices at different concentrations of sucrose.
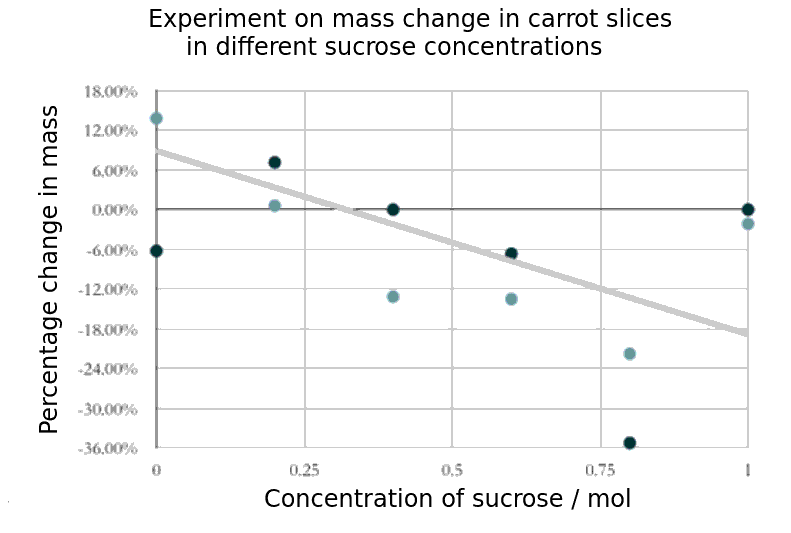
Which of the following is the best estimate of the molarity of the cytoplasm of these cells?
When a sample of cells show no change in mass, then the net movement of water by osmosis must be zero. This shows the concentration of the cytoplasm of the cells. In this graph it would be about 0.3 mol
Which property of phospholipid molecules describes the fact that they have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts?
Phospholipids form bilayers in water due to the amphipathic properties of phospholipid molecules. The hydrophobic tails attract each other and the hydrophilic phosphates are attracted to the water.
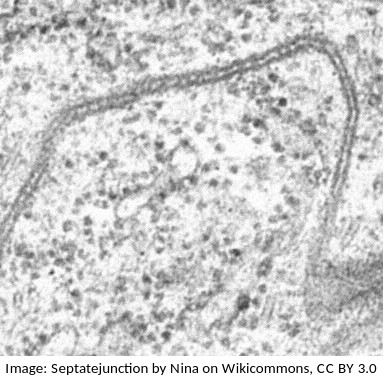 The photograph is from an electron microscope image of a membranes.
The photograph is from an electron microscope image of a membranes.
Parallel dark lines are clearly seen.
In electron micrography, heavy metal stains are often used to enhance contrast. DNA and Proteins often show as dark areas because these molecules can attach to the stain.
Which of the following interpretations is most similar to the proposal of the Daveson-Danielli model of membranes?
Students are expected to know how to use evidence from electron microscopy to support an idea about membranes. One illustration of this is the proposal of the Davson-Danielli model.
Further evidence lead to the falsification of the Davson-Danielli model and the proposal of the fluid mozaic model.
How does compartmentalisation by their internal membranes benefit eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryote cells (approx. 100µm in diameter) are much larger than prokaryote cells (approx 1µm) and so the concentration of reactants in the cytoplasm would be more dilute if all the metabolism happened in the cytoplasm.
Specialist organelles, like mitochondria keep the enzymes for aerobic respiration in one place, which increases their concentration, and increases the rate of reactions.
The 'Cell theory' explains the nature of living things.
Which statement best describes Cell theory?
According to cell theory, living organisms are composed of cells.
Cells come from pre-existing cells and cells are the smallest using of life.
When nerve cells form brain tissue they can; store memories, create thoughts and coordinate movement.
If you only ever studied individual nerve cells you would never see these abilities which the brain has.
What is this type of property called?
Multicellular organisms have properties that emerge from the interaction of their cellular components. (Emergent properties)
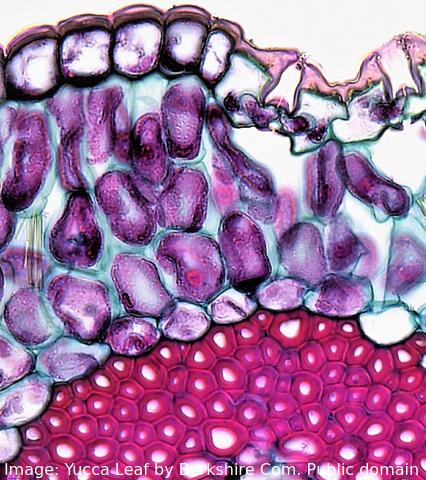 The image shows a range of different cell types in the leaf of a Yucca plant.
The image shows a range of different cell types in the leaf of a Yucca plant.
How do stem cells form this range of cells?
What is the process called?
Specialised tissues can develop by cell differentiation in multicellular organisms.
Differentiation involves the expression of some genes and not others in a cell.
Which of the following could be used to distinguish a living from a non- living object
Comment: Inanimate objects can move, produce and utilise energy but the process of respiration is exclusive to living systems
Which of the following are methods by which molecules can move across membranes?
I. Simple diffusion
II. Facilitated diffusion
III. Cytokinesis
IV. Active transport
There are actually four types of membrane transport which are required in DP Biology, Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis and active transport.
The image shows a cross section of trachea epithelium tissue. What is the best definition of a tissue?

A tissue may have one cell type or several and may have one or more functions. Tracheal epithelium has goblet cells to secrete mucus and columnar epithelial cells with cilia to remove contaminants and pathogens from the air and sweep them away from the lungs.
What is the sequence of events that occur in a cell that is secreting a protein hormone?
1 Exocytosis
2 Vesicle formed by Golgi Body
3 Fusion of vesicle to plasma membrane
4 RER manufactures protein.
Ribosomes on the RER manufacture protein. This is packaged in vesicles by the Golgi Body and moves to the surface of the cell where the vesicle and plasma membrane fuse and exocytosis of the protein occurs.
A mitotic index taken from this microphotograph only would not be regarded as valid. How can a valid count be made?

Which property of stem cells is important for embryonic development?
Stem cells can divide and differentiate along different pathways. For a single fertilised egg cell to grow into an embryo both these processes are necessary.
The theory of spontaneous generation has been disproved by Pasteur's experiment. Is there a point in evolution when spontaneous generation did occur?
The first cells must have arisen spontaneously from non-living matter, probably in volcanic vents, but the universal nature of cell ultrastructure and of the genetic code makes it likely that this only happened once.
In which ways is a plasma membrane fluid?
I The shape is flexible
II Proteins can move in and out of the membrane
III Proteins can move within the membrane
IV It can reseal a small puncture.
The membrane can reseal if slightly damaged and the shape is flexible. Proteins cannot move in and out of the membrane but can move within the membrane.
Which component of the plasma membrane varies in function between differentiated cells?
The protein component of the membrane varies in structure and function.
Which of the following contributed to the acceptance of the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure of Singer and Nicholson in place of the original Davison-Danielli model?
I Hydrophobic membrane proteins
II Irregular sizes of membrane proteins
III Increased magnification of light microscopes.
IV Fluorescent antibody tagging.
The irregular sizes and insolubility of hydrophobic membrane proteins indicated that they could not be a surface layer as proposed by Davison-Danielli. This was confirmed by fluoresecent antibodies showing that proteins were both within and on the membrane.
The image below was taken in 1825 and shows part of the cell cycle.
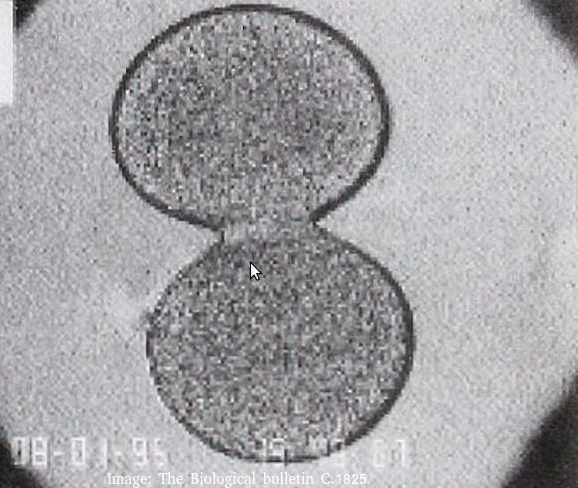
What is shown in the image?
Cytokinesis occurs after mitosis in plant and animal cells.
Animal cells form a cleavage furrow (looks like a wasps waist) as they don't have cell walls.
The two daughter cells are the same size, so cytokinesis is equal.
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.

 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn