Topic 1: Cell biology 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about cell biology.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Cell biology revision resources
This page lists the understandings and skills expected for Topic 1 and links to the sub-topic pages which contain detailed revision notes, activities and past paper style questions. Great for revision.
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
Which cells are produced when a diploid cell divides by mitosis?
Mitosis is division of the nucleus into two genetically identical daughter nuclei in eukaryote cells.
A diploid cell will produce two diploid daughter cells in one division of mitosis.
The four cells shown below have each been surrounded by a solution for 1 hour.
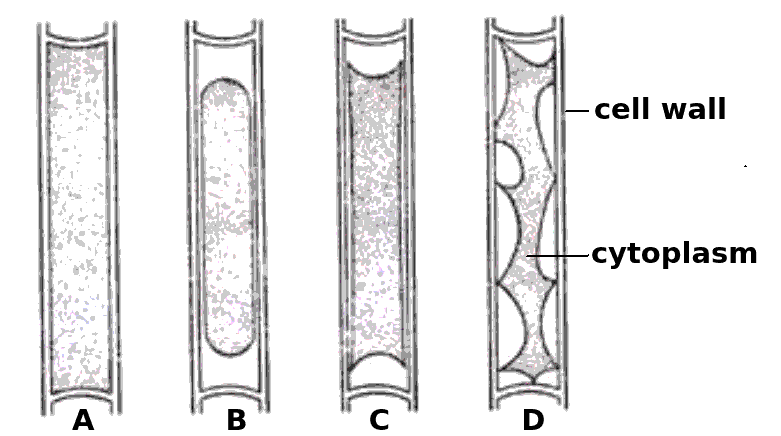
Which cells have been in a hypertonic solution ?
Cell A is swollen turgid, it is in a hypotonic solution or an isotonic solution.
The cells B, C and D show increasing signs of plasmolysis, and so they must be in hypertonic solutions.
Skill: Estimation of osmolarity in tissues by bathing samples in hypotonic and hypertonic solutions. (Practical 2)
The graph below shows the % change in mass of carrot parenchyma slices at different concentrations of sucrose.
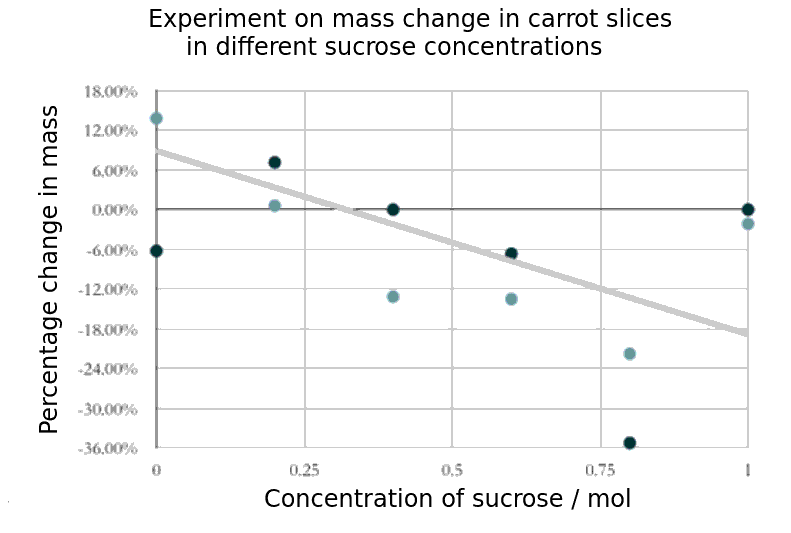
Which of the following is the best estimate of the molarity of the cytoplasm of these cells?
When a sample of cells show no change in mass, then the net movement of water by osmosis must be zero. This shows the concentration of the cytoplasm of the cells. In this graph it would be about 0.3 mol
The electron microscope image below shows an organelle found in eukaryote cells.
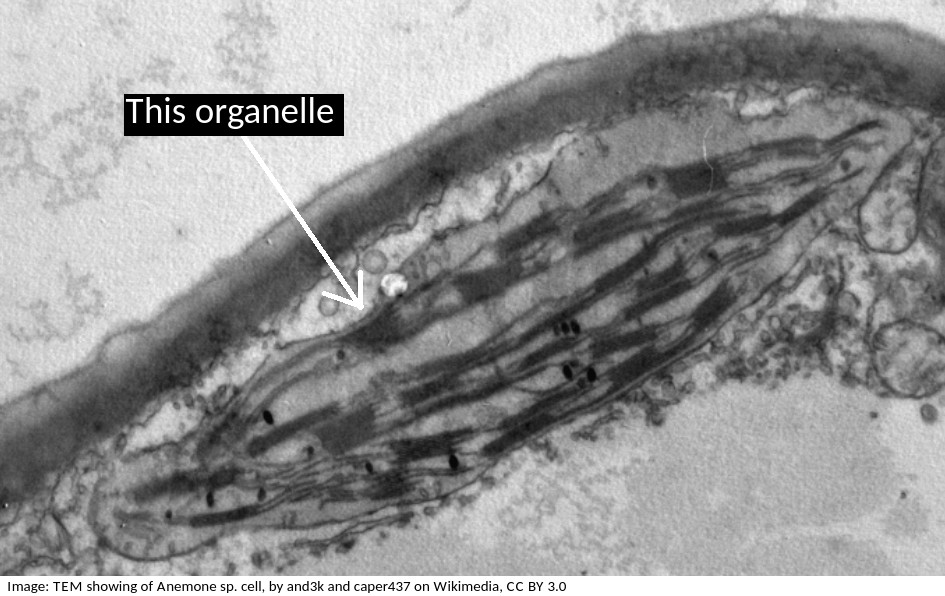
What is the name of the organelle?
Chloroplasts are distinctive because they have stacks of membranes inside, called grana, which hold the chlorophyll that absorbs light.
If you found a eukaryote cell in an electron microscope image, and it contained a lot of rER, Golgi apparatus and many darkly stained vesicles, what do you think the function of the cell is most likely to be?
(eg. goblet cells which make mucus (a protien) will contain lots of rER and vesicles of musus, and palisade mesophyll cells which do photosynthesis will contain lots of chloroplasts)
This electron microscope image shows a group of prokaryotes.
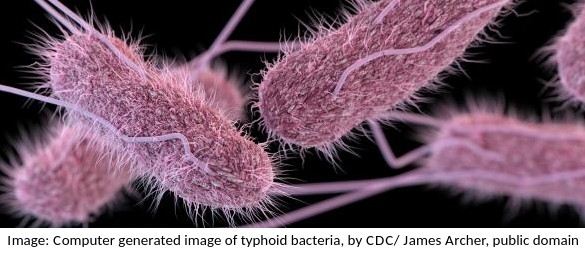
What structures are most likely to be found inside these cells?
Skill: you should know how to draw prokaryotic cells (with a cell wall, plasma membrane, cytoplasm, pili, flagella, 70s ribosomes and nucleoid.) and eukaryotic cells (free 80s ribosomes, rough endoplasmic reticulum (rER), lysosome, Golgi apparatus, mitochondrion and nucleus)
Cell theory covers most, but not all cases.
Which one of these statements is an exception?
Exceptions to cell theory are : multinucleated striated muscle the giant single celled Acetabularia algae?
Also, organisms consisting of only one cell carry out all functions of life in that cell. e.g. Paramecium, Chlorella.
When nerve cells form brain tissue they can; store memories, create thoughts and coordinate movement.
If you only ever studied individual nerve cells you would never see these abilities which the brain has.
What is this type of property called?
Multicellular organisms have properties that emerge from the interaction of their cellular components. (Emergent properties)
Stargardts disease is vision loss caused by the death of both cone cells and rod cells in the part of the retina around the fovea. One potential treatment for Stargardts disease is the use of human embryonic stem cells.
What are the properties of these stem cells, which other cells don't have, that makes them so useful for this treatment?
Stem cells can divide and this help researchers to grow them in the lab.
They can differentiate along different pathways in embryonic development which makes stem cells useful for therapeutic uses (e.g. Stargart's disease) because they can be grown into many different tissues.
The blood cells below were imaged using an electron microscope.
The magnification is x3000 and the ruler measures the central cell as being 2 cm in diameter.
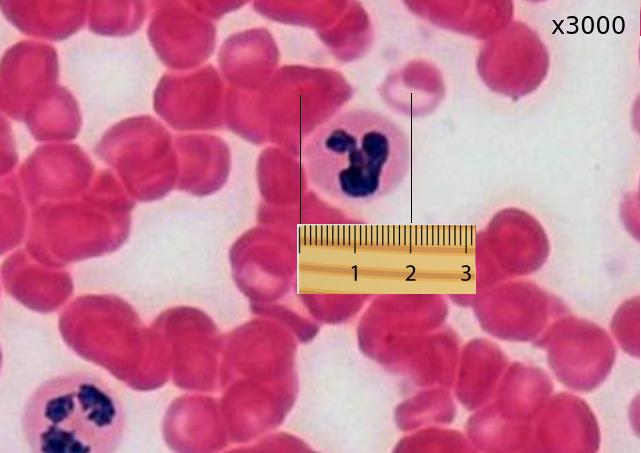
Estimate the actual size of this white blood cell.
Calculate specimen size using magnification?
First change the size measurement into µm units = 20000µm
Then divide by the magnification. 20000 / 3000 = 20 / 3 = 6.6 µm
The 64 codons in the genetic code give rise to the same amino acids in nearly all organisms.
There is very little variation. This is evidence for a single common origin of life.
Differences in the frequency of amino acid use reflects the different genes in the two organisms.
Which two processes are involved in cell differentiation?
Comment: During differentiation genes may be activated or repressed causing the formation of different proteins by the ribosomes but other organelles such as mitochondria continue to function in the same way
Which is the correct order of SI units, beginning with the largest?
Comment: SI units always have a differential of 1000. The unit without the prefix is the standard SI unit (metre, m). B and D are clearly wrong, eliminate those answers first.
The image below is of Dracaena leaf upper epidermis cells.
Which of the following is the best estimate of the length (from top to bottom) of an epidermal cell?
Comment: The cells are approximately the same size as the scale bar.
This would make 70µm the closest estimate.
The diagram shows a typical eukaryotic plant cell. Which organelles are involved in supporting the cell and plant? I Cell wall II Cytoplasm III Nucleus IV Vacuole.

The cell and plant are supported by the turgor pressure of water in the vacuole acting on the rigid cell wall.
Which organelles are found in large numbers in secretory cells in animals? I Vesicles II Golgi Body III Mitochondria IV Rough endoplasmic reticulum.

Secretory cells synthesise proteins for exocytosis so have large numbers of mitochondria to supply energy, RER to synthesise the proteins for packaging into vesicles by the Golgi Body.
The microphotograph is of stratified epithelium. Cells are produced by mitosis in the area marked 1 and eventually reach the surface to replace lost cells. Which biological processes does this represent?

The cells produced by mitosis differentiate into mature cells and replace the cells lost at the surface.
Which means of transport across a plasma membrane requires the molecule shown in the picture?

Which organelles in a plant cell are believed to have originated as free-living prokaryotic cells?

Both the mitochondria and the chloroplast in plant cells are thought to have been free-living prokaryotes which evolved in a symbiotic relationship with a eukaryotic cell.
Which is the best description of the genetic code?
The genetic code is universal (the codons code for the same amino acid in all organisms) but there are a very few exceptions, mostly in Archaea. A mutation does not alter the genetic code, it alters the base sequence of DNA.
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.

 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn