Topic 1: Cell biology 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about cell biology.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Cell biology revision resources
This page lists the understandings and skills expected for Topic 1 and links to the sub-topic pages which contain detailed revision notes, activities and past paper style questions. Great for revision.
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
Huntington's Disease (HD) is a brain disorder that affects a person's ability to talk, and move. HD is caused by a faulty protein. The job of the protein is to direct vesicles containing important molecules to the outside of the cell. The chemicals are released when the vesicle reaches the membrane.
What is the name given to the release of chemicals by a cell in this way?
This is a type of secretion, the vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane and its contents are released. This is called "exocytosis".
What is the best definition of endosymbiosis?
Endosymbiosis is where a cell engulfs another cell and it continues to live inside the cell.
The engulfed cell provides something for the host cell, and gets something in return. Both cells benefit.
The image below shows a eukaryotic cell.
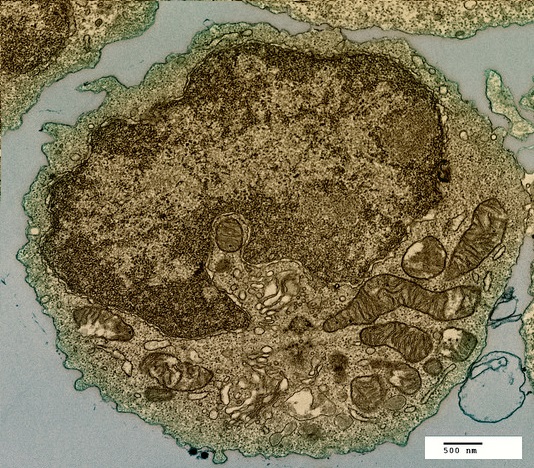
Which structure, visible in the image, could be used as evidence supporting endosymbiosis?
The mitochondria provide evidence supporting endosymbiosis because they have:
- a double membrane
- 70S ribosomes
- DNA
The 64 codons in the genetic code give rise to the same amino acids in nearly all organisms.
There is very little variaion. This is evidence for a single common origin of life.
Differences in the frequency of amino acid use reflects the different genes in the two organisms.
During interphase of the cell cycle what happens to the DNA in the nucleus?
Under the microscope there is little change during interphase.
However interphase is a very active phase of the cell cycle with many processes occurring in the nucleus and cytoplasm. (It is subdivided into G1, S, G2 phases of the cell cycle)
DNA replication occurs during the S-phase.
Sodium channels are made from a protein.
Where in the cell are sodium channel proteins found?
Sodium channel proteins are found spanning the plasma membrane. Their structure helps the function for facilitated diffusion in cells because they allow ions to pass cross the membrane.
If the protein was not a trans-membrane protein then it would not be able to transport ions across the membrane.
The graph below shows the % change in mass of carrot parenchyma slices at different concentrations of sucrose.
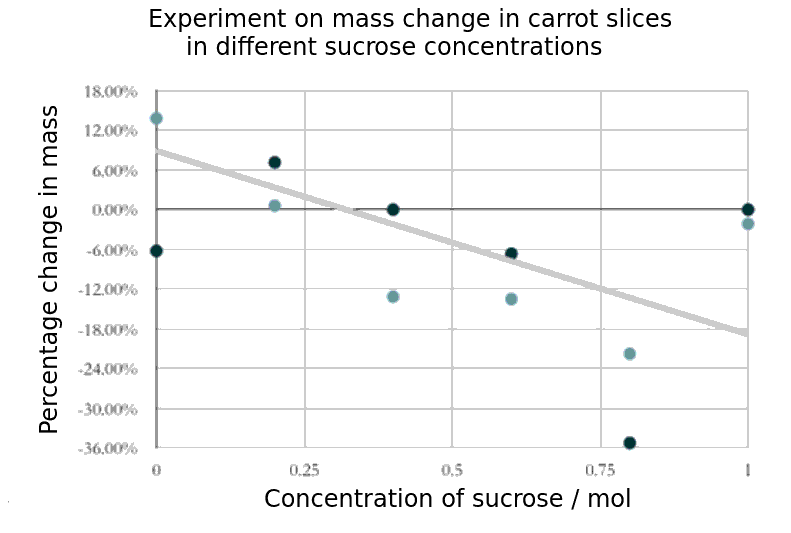
Which of the following is the best estimate of the molarity of the cytoplasm of these cells?
When a sample of cells show no change in mass, then the net movement of water by osmosis must be zero. This shows the concentration of the cytoplasm of the cells. In this graph it would be about 0.3 mol
The electron microscope image below shows three organelles found in an animal cell.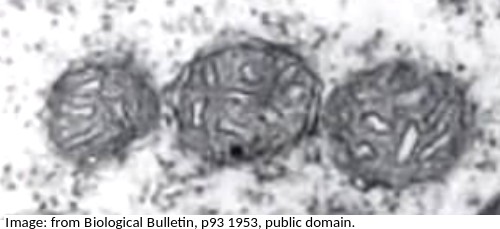
What is the name of the organelles?
Know how to idenfity the organelles in eukaryotes and draw their compartmentalised structure.
A mitochondrion (pleural = mitochondria) has an outer membrane and inner membrane folded into long thing 'flaps' called cristae.
The electron microscope image below shows a ciliated epithelial cell from the trachea.
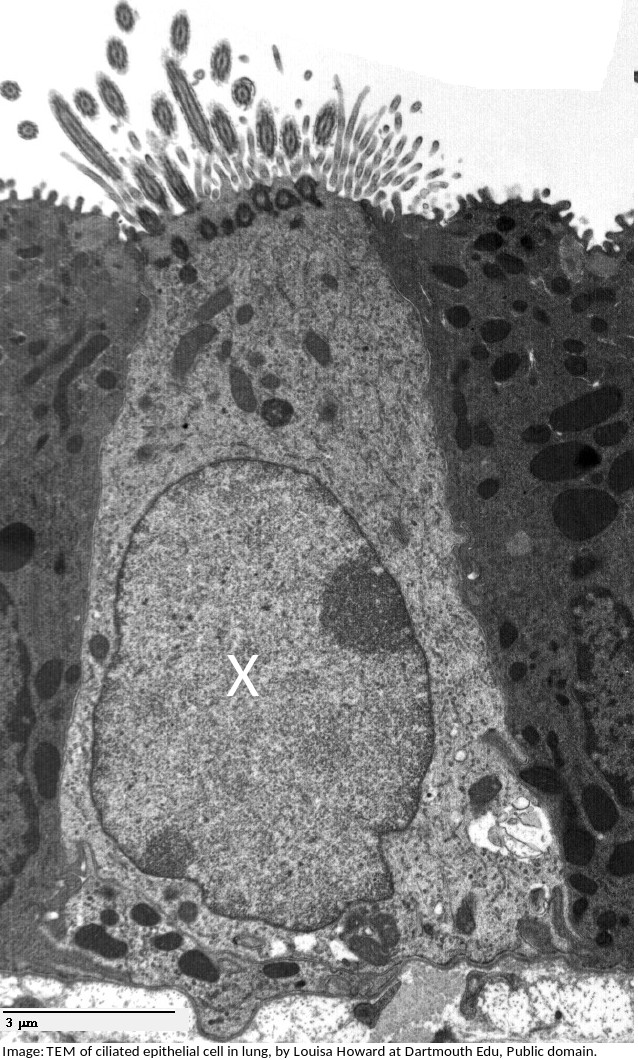
What is the name of the organelle labelled X?
How does compartmentalisation by their internal membranes benefit eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryote cells (approx. 100µm in diameter) are much larger than prokaryote cells (approx 1µm) and so the concentration of reactants in the cytoplasm would be more dilute if all the metabolism happened in the cytoplasm.
Specialist organelles, like mitochondria keep the enzymes for aerobic respiration in one place, which increases their concentration, and increases the rate of reactions.
The blood cells below were imaged using an electron microscope.
The magnification is x3000 and the ruler measures the central cell as being 2 cm in diameter.
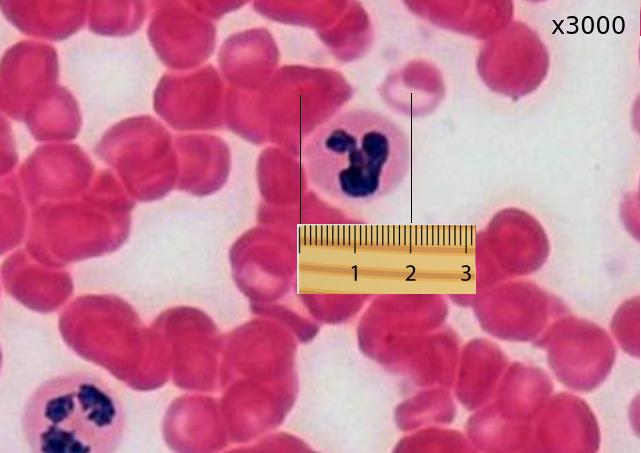
Estimate the actual size of this white blood cell.
Calculate specimen size using magnification?
First change the size measurement into µm units = 20000µm
Then divide by the magnification. 20000 / 3000 = 20 / 3 = 6.6 µm
Cells are often stored in isotonic conditions because they can be damaged in other concentrations, hypertonic, or hypotonic. Which of the descriptions of hypertonic is the most accurate?
Hypertonic solutions have a higher concentration of solutes, and lower water potentials than cells.
Which label in the image below shows the process of endocytosis?
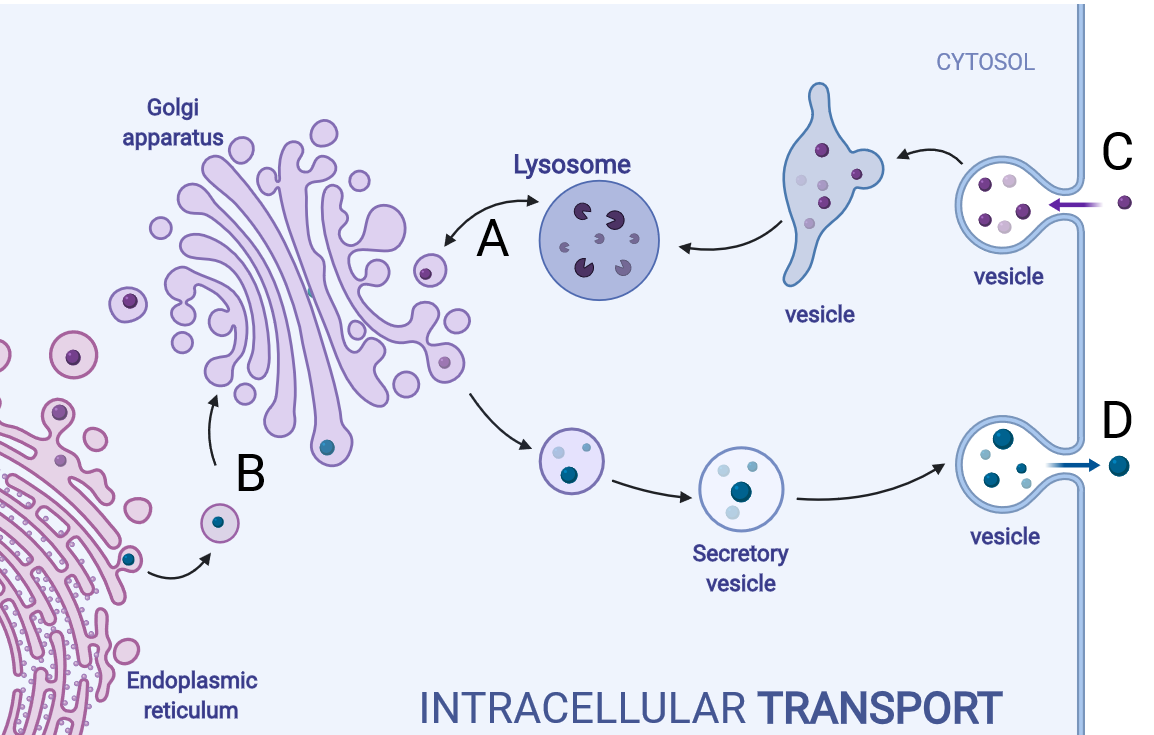
Endocytosis is the process where a substance is surrounded by the plasma membrane which forms a vesicle inside the cell that then moves into the cytoplasm, separating from the plasma membrane.
Which is the correct order of SI units, beginning with the largest?
Comment: SI units always have a differential of 1000. The unit without the prefix is the standard SI unit (metre, m). B and D are clearly wrong, eliminate those answers first.
What is the approximate length of the bacterial cell in the image?

The scale bar is 1 µm and the bacterium is approximately 3 times the length of the scale bar.
Which organelle in a eukarytotic animal cell synthesises proteins for exocytosis?

The RER synthesises proteins for exocytosis.
The image is of a prokaryotic cell. Which feature defines the cell as prokaryotic?

The lack of a membrane bound nucleus (nucleoid) classifies a cell as prokaryotic.
Which organelle is visible in an electron microscope but not in a light microscope?

The ribosome is too small to be seen in the electron microscope, the other organelles were seen in the light microscope before the electron microscope was invented.
A mitotic index taken from this microphotograph only would not be regarded as valid. How can a valid count be made?

In which ways is a plasma membrane fluid?
I The shape is flexible
II Proteins can move in and out of the membrane
III Proteins can move within the membrane
IV It can reseal a small puncture.
The membrane can reseal if slightly damaged and the shape is flexible. Proteins cannot move in and out of the membrane but can move within the membrane.
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.

 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn