Topic 1: Cell biology 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about cell biology.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Cell biology revision resources
This page lists the understandings and skills expected for Topic 1 and links to the sub-topic pages which contain detailed revision notes, activities and past paper style questions. Great for revision.
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
Pasteur's experiment with 'swan neck' flasks showed that a sterile nutrient medium exposed to the air would not show any signs of bacterial growth under his conditions.
What prevented the growth of bacteria?
Pasteur's famous experiments with swan neck flasks showed that broth kept in a flask where no dust could settle in the nutrient medium, and thus no living cells could get in, would not go mouldy.
This disproved the theory of spontaeous generation.
Cells today come from pre-existing cells. The origin of the fist cell must be different.
Where do biologists think the first cell came from?
The first cell must have come from non-living material. This material must have contained molecules which today we consider as organic, carbon containing molecules.
Identify the stage of mitosis for the two cells X and Y.
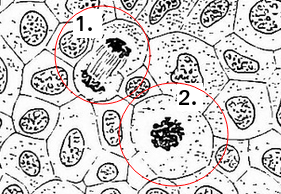
Skill: Identification of phases of mitosis in cells viewed with a microscope or in a micrograph
(prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase).
The graph below shows the % change in mass of carrot parenchyma slices at different concentrations of sucrose.
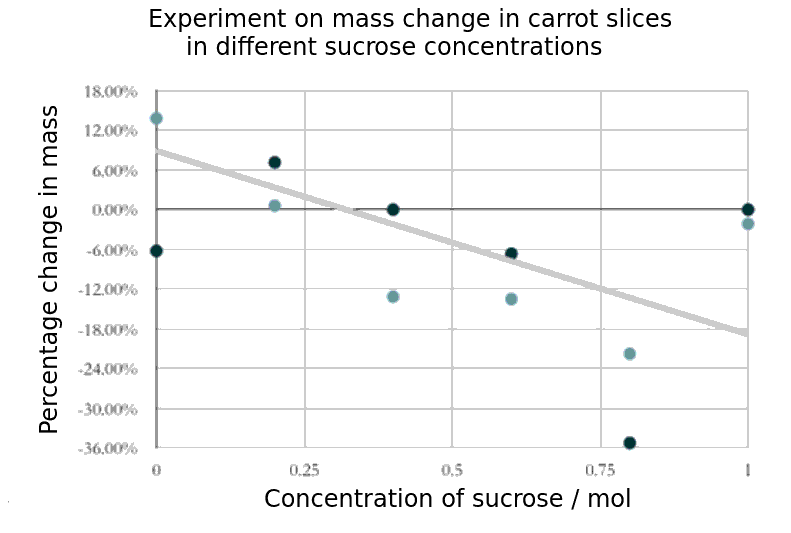
Which of the following is the best estimate of the molarity of the cytoplasm of these cells?
When a sample of cells show no change in mass, then the net movement of water by osmosis must be zero. This shows the concentration of the cytoplasm of the cells. In this graph it would be about 0.3 mol
The electron microscope image below shows an organelle found in both animal and plant cells.

What is the name of the organelle?
Know how to idenfity the organelles in eukaryotes and draw their compartmentalised structure.
The rER has parallel membranes covered in dots, which are ribosomes, used for making proteins, for secretion from the cell.
The electron microscope image below shows a ciliated epithelial cell from the trachea.
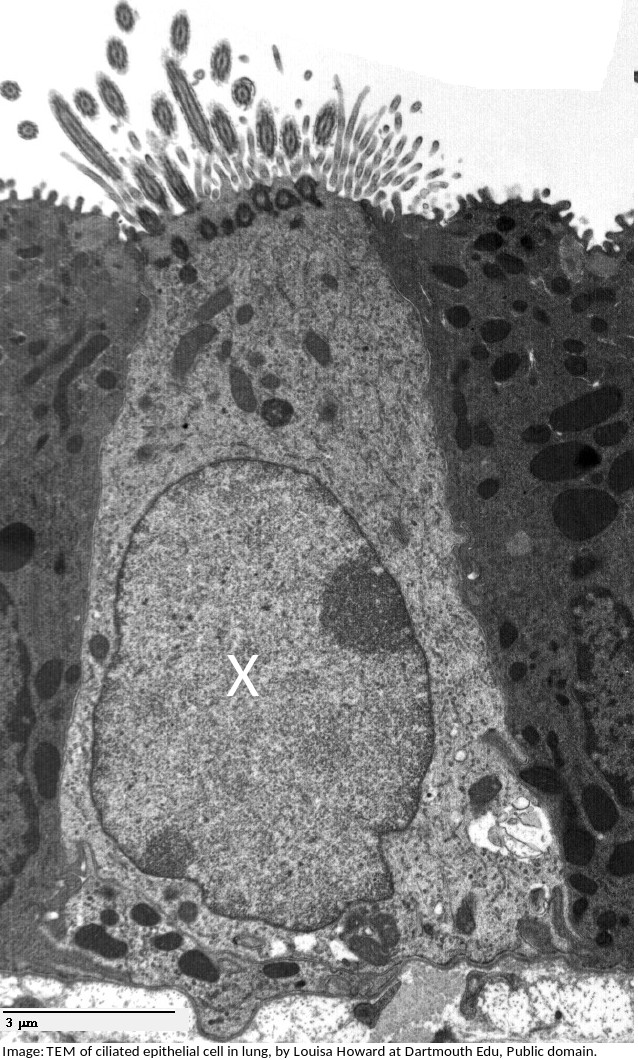
What is the name of the organelle labelled X?
The electron microscope image below shows a cell.
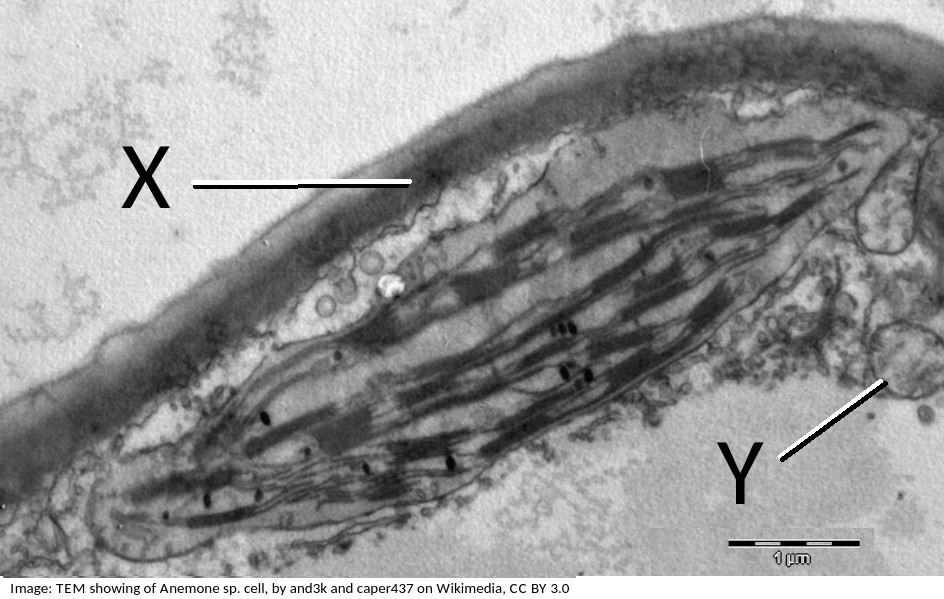
What are the organelles shown by the labels X & Y?
If you look closely at X, it points to the cell wall, outside the plasma membrane, it is close to the plasma membrane, but not touching the chloroplast.
The pale area below Y is the vacuole.
Organelle Y is a mitochondrion, you can tell this by its size, and the presence of membranes inside.
If you know someone with a disease that might be cured by stem cell therapy then you might be a supporter of this research. You probably also know that some other people have deep concerns.
Which of the following is not a potential benefit of the use of stem cells?
There are ethical concerns about the use of embryo stem cells.
The research is expensive, and potential treatments are also likely to be expensive, and probably not available to all.
Many people who are against stem cells say that it is because cells are taken from human embryos, which have the potential for human live, and should be protected. There are other sources of stem cells, they argue.
Which of the structures listed below are involved in membrane transport?
Many transmembrane proteins are involved in transport of molecules across membranes. These can either provide a sort of molecular pore through which ions or molecules can pass (facilitated diffusion), or they can use ATP to actively move molecules, even against the concentration gradient (active transport).These are just two examples, transport can also occur by simple diffusion through the phospholipid bilayer, or by endocytosis.
Which two processes are involved in cell differentiation?
Comment: During differentiation genes may be activated or repressed causing the formation of different proteins by the ribosomes but other organelles such as mitochondria continue to function in the same way
Which is the correct order of SI units, beginning with the largest?
Comment: SI units always have a differential of 1000. The unit without the prefix is the standard SI unit (metre, m). B and D are clearly wrong, eliminate those answers first.
The image shows a cross section of trachea epithelium tissue. What is the best definition of a tissue?

A tissue may have one cell type or several and may have one or more functions. Tracheal epithelium has goblet cells to secrete mucus and columnar epithelial cells with cilia to remove contaminants and pathogens from the air and sweep them away from the lungs.
What best describes the organism in the light microscope image?

It is unicellular (one cell) and a eukaryote (has a nucleus) and not autotrophic.
Why is a fungal hypha an exception to the cell theory?

A fungal hypha has many nuclei in a hypha but no cross walls to divide the hypha into cells.
The image shows a transverse section of a plant cell seen using an electron microscope.
What is the main function of the large organelle (A) seen in the cell?

The organelle shown is the nucleus, it stores the genetic information, DNA and is the location of DNA replication and Transcription.
Protein channels cross the membrane to allow hydrophilic substances to pass through the membrane.
The diagram is of a plasma membrane. Which label corresponds to the hydrophilic area of an amphipathic molecule?

Protein (5) has both hydrophilic and hydrophobic areas to act as an integral protein. The central channel is hydrophilic.
What tonicity should a saline drip have in comparison to human blood?

The saline drip must be isotonic to human blood to not cause water gain or loss from tissues.
Louis Pasteur used sterile broth and swan necked flasks to disprove which theory?

Pasteur demonstrated that broth would go cloudy only when air was allowed to contact the broth, bringing microbes. He disproved Spontaneous Generation.
Which of the following contributed to the acceptance of the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure of Singer and Nicholson in place of the original Davison-Danielli model?
I Hydrophobic membrane proteins
II Irregular sizes of membrane proteins
III Increased magnification of light microscopes.
IV Fluorescent antibody tagging.
The irregular sizes and insolubility of hydrophobic membrane proteins indicated that they could not be a surface layer as proposed by Davison-Danielli. This was confirmed by fluoresecent antibodies showing that proteins were both within and on the membrane.
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.


 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn