Topic 1: Cell biology 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about cell biology.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Cell biology revision resources
This page lists the understandings and skills expected for Topic 1 and links to the sub-topic pages which contain detailed revision notes, activities and past paper style questions. Great for revision.
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
The image below shows a eukaryotic cell.
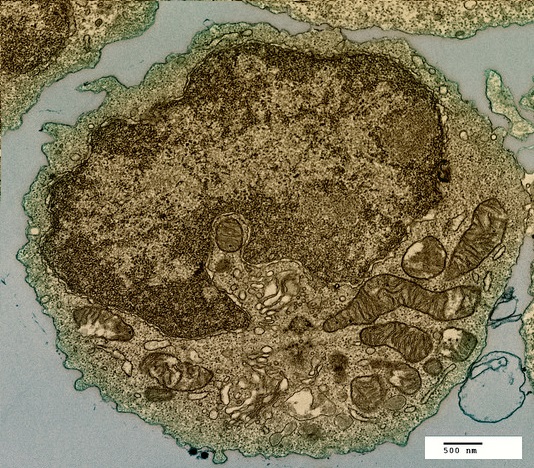
Which structure, visible in the image, could be used as evidence supporting endosymbiosis?
The mitochondria provide evidence supporting endosymbiosis because they have:
- a double membrane
- 70S ribosomes
- DNA
The 64 codons in the genetic code give rise to the same amino acids in nearly all organisms.
There is very little variaion. This is evidence for a single common origin of life.
Differences in the frequency of amino acid use reflects the different genes in the two organisms.
Which one of the statements below best describes the mitotic index?
The mitotic shows the speed of cell division, which can be used as a tool to identify cancer.
It is calculated by dividing the number of cells doing mitosis by the total number of cells.
The microscope image shows cells in a tissue sample taken from a growth suspected of being cancerous.
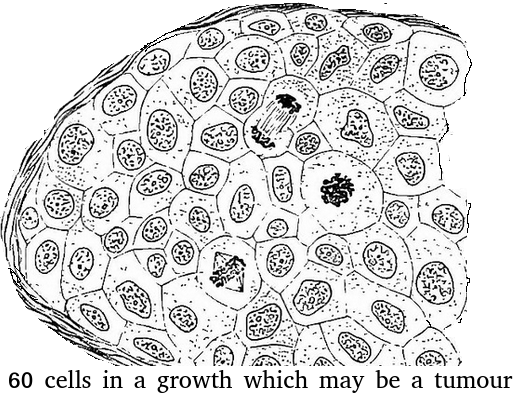
What is the best estimate of the mitotic index of this tissue?
Assume that there are exactly 60 cells (for simplicity).
Skill: Determination of a mitotic index from a micrograph
There are 3 cells in stages of mitosis.
So the mitotic index = 3 divided by 60 cells total.
Keeping it simple = 1 / 20 or 0.05
Which property of phospholipid molecules describes the fact that they have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts?
Phospholipids form bilayers in water due to the amphipathic properties of phospholipid molecules. The hydrophobic tails attract each other and the hydrophilic phosphates are attracted to the water.
The illustration shown below is of a protein (green) attached to a membrane.
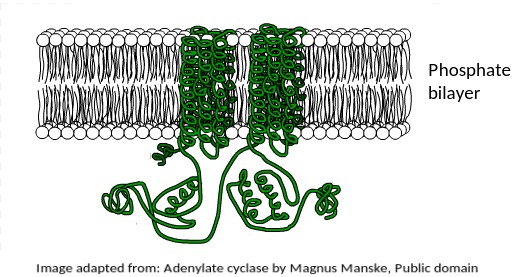
What is the most likely function of this membrane protein?
This protein is found in the human liver, where the hormone adrenaline indirectly stimulates it to mobilise stored energy inside liver cells in the "fight or flight" response.
The fact that it is a transmembrane protein is essential for this function.
It is interesting to note that this protein is also secreted by Anthrax bacteria as a toxin.
It upsets the metabolism of host cells when it enters them.
Why is it that prokaryotes can divide by the simple process of binary fission, but eukaryotes have to divide by the more complex process of mitosis?
To explain how the structure of prokaryotes allows them to divide by binary fission you could mention:
- Prokaryotes have a single chromosome, eukaryotes have multiple chromosomes
- Prokaryotes have no nuclear membrane, which eukaryotes have.
How does compartmentalisation by their internal membranes benefit eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryote cells (approx. 100µm in diameter) are much larger than prokaryote cells (approx 1µm) and so the concentration of reactants in the cytoplasm would be more dilute if all the metabolism happened in the cytoplasm.
Specialist organelles, like mitochondria keep the enzymes for aerobic respiration in one place, which increases their concentration, and increases the rate of reactions.
The 'Cell theory' explains the nature of living things.
Which statement best describes Cell theory?
According to cell theory, living organisms are composed of cells.
Cells come from pre-existing cells and cells are the smallest using of life.
The electron microscope image below shows a scale bar marked with 100µm.
The large 'goblet cell' in the centre is producing mucous which will protect the surface of the epithelium.
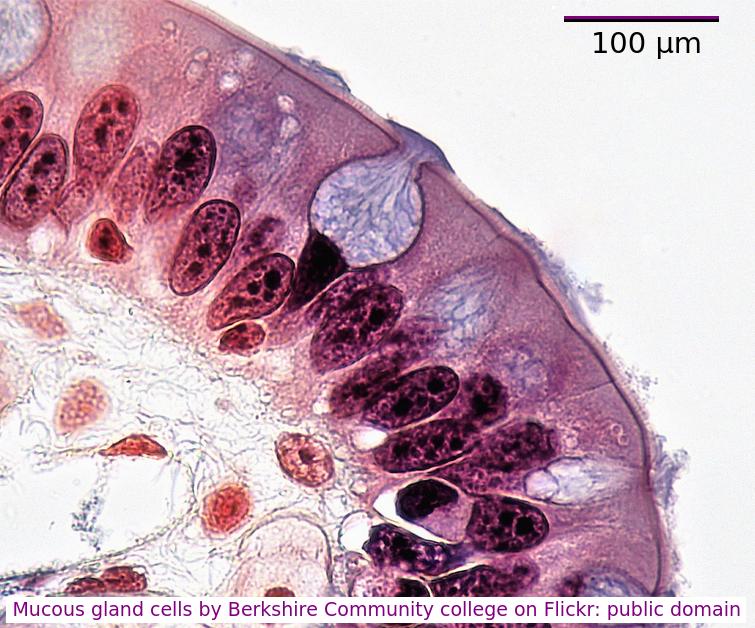
What is the diameter of the goblet cell?
Accurately, measure the scale bar length in mm, measure the diameter of the cell, in mm
divide cell diameter by scalebar and multiply by 100µm.
You can often estimate the size using the scale bar and your thumb or a pen.
Explain the significance of the following terms in Biology; Metabolism, response, growth, reproduction, excretion, nutrition, homeostasis.
Remember MR H GREN. These letters represent the seven characteristics of living things.
The image below is of Dracaena leaf upper epidermis cells.
Which of the following is the best estimate of the length (from top to bottom) of an epidermal cell?
Comment: The cells are approximately the same size as the scale bar.
This would make 70µm the closest estimate.
The image shows a transverse section of a plant cell seen using an electron microscope.
What is the main function of the large organelle (A) seen in the cell?

The organelle shown is the nucleus, it stores the genetic information, DNA and is the location of DNA replication and Transcription.
The diagram is of a plasma membrane. Which label corresponds to the hydrophilic area of an amphipathic molecule?

Protein (5) has both hydrophilic and hydrophobic areas to act as an integral protein. The central channel is hydrophilic.
The image is of a channel protein. What is the function of a membrane channel protein?

Channel proteins are used for facilitated diffusion down the concentration gradient.
Which process is involved in white blood cells engulfing bacteria (arrowed in the photomicrograph)?

White blood cells engulf bacteria by endocytosis, the intake of solid particles by a cell membrane.
What is the name of the process by which a white blood cell can engulf a pathogenic bacterium?
Endocytosis ("into the cell") is the process by which cells can engulf particles.
In which ways is a plasma membrane fluid?
I The shape is flexible
II Proteins can move in and out of the membrane
III Proteins can move within the membrane
IV It can reseal a small puncture.
The membrane can reseal if slightly damaged and the shape is flexible. Proteins cannot move in and out of the membrane but can move within the membrane.
How do integral proteins remain within the phospholipid bilayer?
Integral proteins have a hydrophobic centre that associates with the fatty acid inner layer of the bilayer and a hydrophilic head that associates with the phospholipid heads.
Why is the cell component in the image regarded as an organelle?

The organelle is a cell component with a membane, the mitochondrion, it is adapted to aerobic respiration.
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.

 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn