Topic 1: Cell biology 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about cell biology.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Cell biology revision resources
This page lists the understandings and skills expected for Topic 1 and links to the sub-topic pages which contain detailed revision notes, activities and past paper style questions. Great for revision.
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
The DNA of eukaryote cells is organised into chromosomes
What happens to the DNA at prophase in the beginning of mitosis?
Chromosomes condense by supercoiling during mitosis. This makes the chromosomes visible.
The DNA replicates during interphase, not prophase.
The graph below shows the % change in mass of carrot parenchyma slices at different concentrations of sucrose.
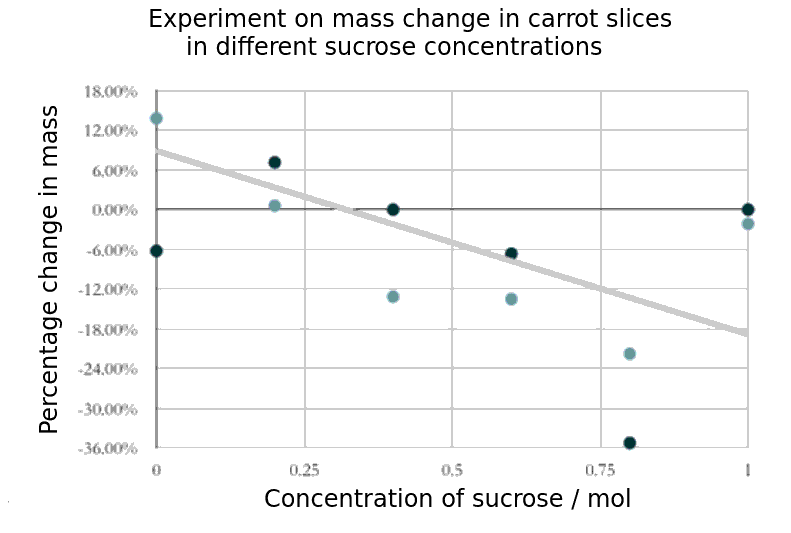
Which of the following is the best estimate of the molarity of the cytoplasm of these cells?
When a sample of cells show no change in mass, then the net movement of water by osmosis must be zero. This shows the concentration of the cytoplasm of the cells. In this graph it would be about 0.3 mol
Which of the following is true of peripheral proteins in cell membranes?
Membrane proteins are diverse in terms of structure, position in the membrane and function.
Peripheral proteins are attached to the membrane but found on its surface.
The image below shows three structures as seen in an electron microscope.
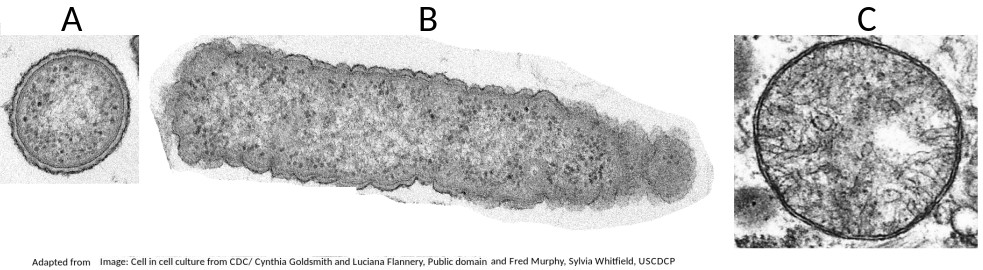
Which of the structures are prokaryote cells?
Students are expected to be able to recognise and draw the simple structure of Prokaryote cells.
There is no compartmentation in prokaryote cells, and as membranes can be seen in structure B (a mitochondrion) it is not a prokaryote.
Why is it that prokaryotes can divide by the simple process of binary fission, but eukaryotes have to divide by the more complex process of mitosis?
To explain how the structure of prokaryotes allows them to divide by binary fission you could mention:
- Prokaryotes have a single chromosome, eukaryotes have multiple chromosomes
- Prokaryotes have no nuclear membrane, which eukaryotes have.
There are seven processes which are said to be possessed by all living things.
This sweet pea plant has grown a tendril around some string, to help support its upward growth.
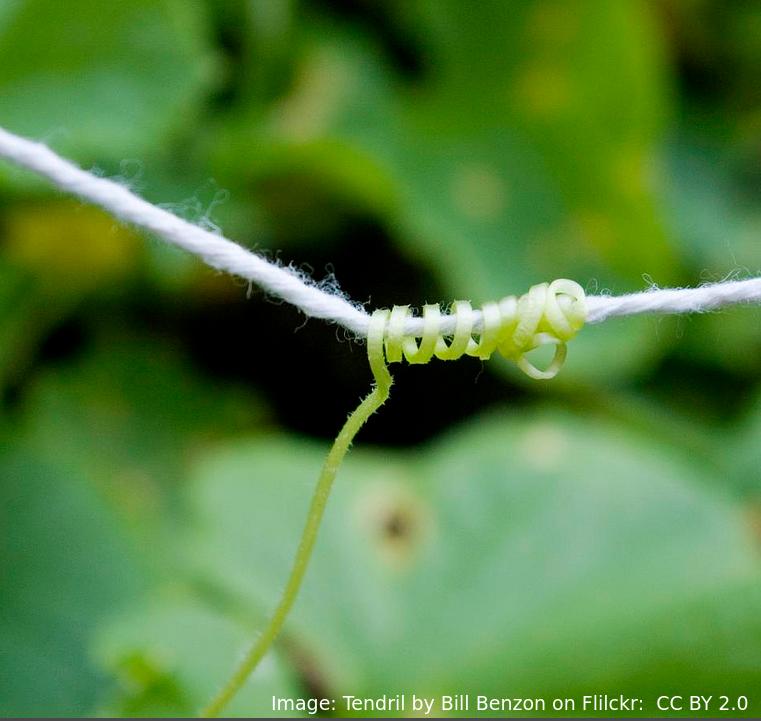

Which of the characteristics of living things is illustrated in this photo?
The characteristics of living things (Mr H. Gren - metabolism, response, , homeostasis, growth, reproduction, excretion & nutrition)
The fly is responding to the closing trap, and the trap has responded to the presence of the fly.
Stargardts disease is vision loss caused by the death of both cone cells and rod cells in the part of the retina around the fovea. One potential treatment for Stargardts disease is the use of human embryonic stem cells.
What are the properties of these stem cells, which other cells don't have, that makes them so useful for this treatment?
Stem cells can divide and this help researchers to grow them in the lab.
They can differentiate along different pathways in embryonic development which makes stem cells useful for therapeutic uses (e.g. Stargart's disease) because they can be grown into many different tissues.
The image is of a prokaryotic cell. Which feature defines the cell as prokaryotic?

The lack of a membrane bound nucleus (nucleoid) classifies a cell as prokaryotic.
Which organelle is visible in an electron microscope but not in a light microscope?

The ribosome is too small to be seen in the electron microscope, the other organelles were seen in the light microscope before the electron microscope was invented.
The diagram is of a plasma membrane. Which label corresponds to an extrinsic glycoprotein?

Extrinsic proteins are on the outside of the membrane, glycoproteins have carbohydrate prosthetic (side) groups (shown by the hexagonal shape).
The diagram is of a plasma membrane. Which label corresponds to the hydrophilic area of an amphipathic molecule?

Protein (5) has both hydrophilic and hydrophobic areas to act as an integral protein. The central channel is hydrophilic.
The image is a ribbon model of a channel protein. Where would this be found in a plasma membrane?

Channel proteins penetrate the membrane and have a central hydrophilic area (yellow in the diagram which is shown from above).
What is the sequence of events that occur in a cell that is secreting a protein hormone?
1 Exocytosis
2 Vesicle formed by Golgi Body
3 Fusion of vesicle to plasma membrane
4 RER manufactures protein.
Ribosomes on the RER manufacture protein. This is packaged in vesicles by the Golgi Body and moves to the surface of the cell where the vesicle and plasma membrane fuse and exocytosis of the protein occurs.
Which is the best description of the genetic code?
The genetic code is universal (the codons code for the same amino acid in all organisms) but there are a very few exceptions, mostly in Archaea. A mutation does not alter the genetic code, it alters the base sequence of DNA.
What is the structure of the genetic material found in a mitochondrion?
Mitochondrial DNA is a single helical molecule, not associated with protein and circular in shape. The same as prokaryote nucleoid DNA.
Identify the stage of mitosis of cells 1 and 2

In cell 2, the chromatids are aligned on the equator (seen from above)- Metaphase. In cell 1, the chromatids are moving towards the poles - Anaphase.
All eukaryote cells have differing combinations of the same types of organelles. How can this be explained?
Similarity in structure and function are taken as evidence of a common ancestor. All of the other statements are partially true but do not provide an explanation.
Which of the following are believed to be endosymbiotic structures involved in cell locomotion in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Flagellae are locomotory structures found in some Monera (bacteria), and some eukaryotic cells such as male gametes and Protoctista. Mitochondria are not found in prokaryotes. Pseudopodia are involved in locomotion but only in cells without an external wall. Fimbriae in bacteria allow for binding to a host or substrate, the same name is given to projections in the oviduct that aid movement of the ovum towards the uterus.
The theory of spontaneous generation has been disproved by Pasteur's experiment. Is there a point in evolution when spontaneous generation did occur?
The first cells must have arisen spontaneously from non-living matter, probably in volcanic vents, but the universal nature of cell ultrastructure and of the genetic code makes it likely that this only happened once.
Which of the following contributed to the acceptance of the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure of Singer and Nicholson in place of the original Davison-Danielli model?
I Hydrophobic membrane proteins
II Irregular sizes of membrane proteins
III Increased magnification of light microscopes.
IV Fluorescent antibody tagging.
The irregular sizes and insolubility of hydrophobic membrane proteins indicated that they could not be a surface layer as proposed by Davison-Danielli. This was confirmed by fluoresecent antibodies showing that proteins were both within and on the membrane.
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.

 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn