Topic 1: Cell biology 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about cell biology.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Cell biology revision resources
This page lists the understandings and skills expected for Topic 1 and links to the sub-topic pages which contain detailed revision notes, activities and past paper style questions. Great for revision.
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
Huntington's Disease (HD) is a brain disorder that affects a person's ability to talk, and move. HD is caused by a faulty protein. The job of the protein is to direct vesicles containing important molecules to the outside of the cell. The chemicals are released when the vesicle reaches the membrane.
What is the name given to the release of chemicals by a cell in this way?
This is a type of secretion, the vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane and its contents are released. This is called "exocytosis".
Cells today come from pre-existing cells. The origin of the fist cell must be different.
Where do biologists think the first cell came from?
The first cell must have come from non-living material. This material must have contained molecules which today we consider as organic, carbon containing molecules.
The image below shows a eukaryotic cell.
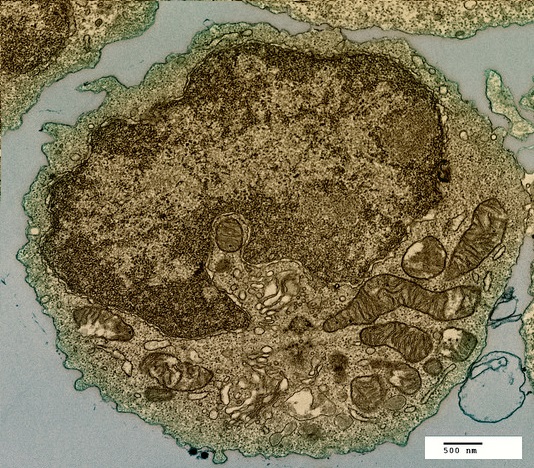
Which structure, visible in the image, could be used as evidence supporting endosymbiosis?
The mitochondria provide evidence supporting endosymbiosis because they have:
- a double membrane
- 70S ribosomes
- DNA
The DNA of eukaryote cells is organised into chromosomes
What happens to the DNA at prophase in the beginning of mitosis?
Chromosomes condense by supercoiling during mitosis. This makes the chromosomes visible.
The DNA replicates during interphase, not prophase.
The image below was taken in 1825 and shows part of the cell cycle.
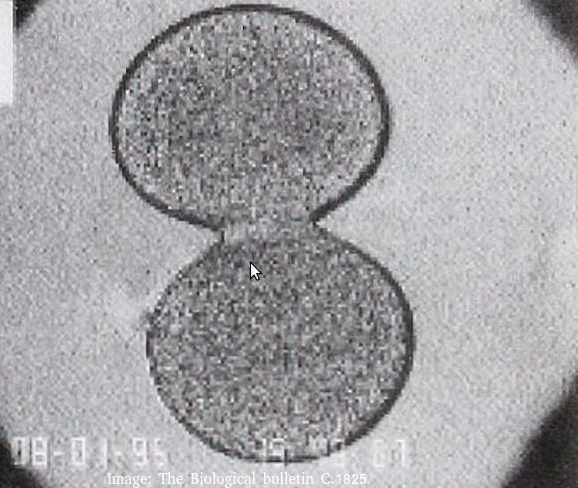
What type of cells is this and at which stage of the cell cycle?
Cytokinesis occurs after mitosis in plant and animal cells. The chromosomes are uncoiled.
Plant cells build a new cell wall which divides the cytoplasm.
Animal cells form a cleavage furrow (likes a wasps waist) as they don't have cell walls.
This box contains a lung waiting for a transplant operation.
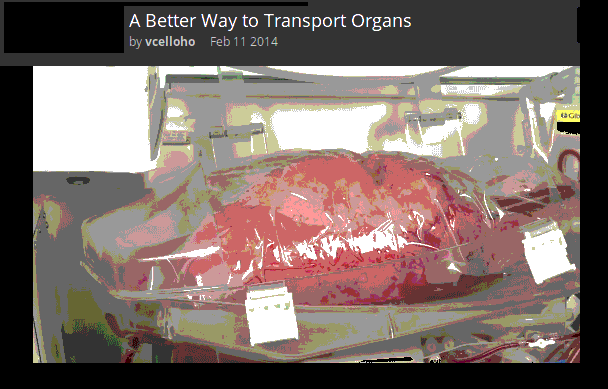
What is special about the solution inside the box which surrounds the tissue?
Tissues and organs must be kept in a solution with the same osmolarity as the cytoplasm of the cells to prevent osmosis. If they were kept in pure water, osmosis would carry water into the cells and they would burst, causing damage to the cells. If the solution was hypertonic, the tissue would lose water (and gain ions).
The four cells shown below have each been surrounded by a solution for 1 hour.
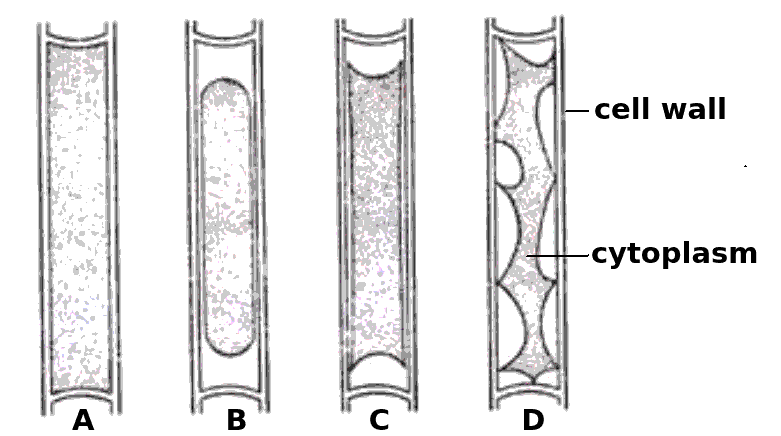
Which cells have been in a hypertonic solution ?
Cell A is swollen turgid, it is in a hypotonic solution or an isotonic solution.
The cells B, C and D show increasing signs of plasmolysis, and so they must be in hypertonic solutions.
Skill: Estimation of osmolarity in tissues by bathing samples in hypotonic and hypertonic solutions. (Practical 2)
The electron microscope image below shows an organelle found in eukaryote cells.
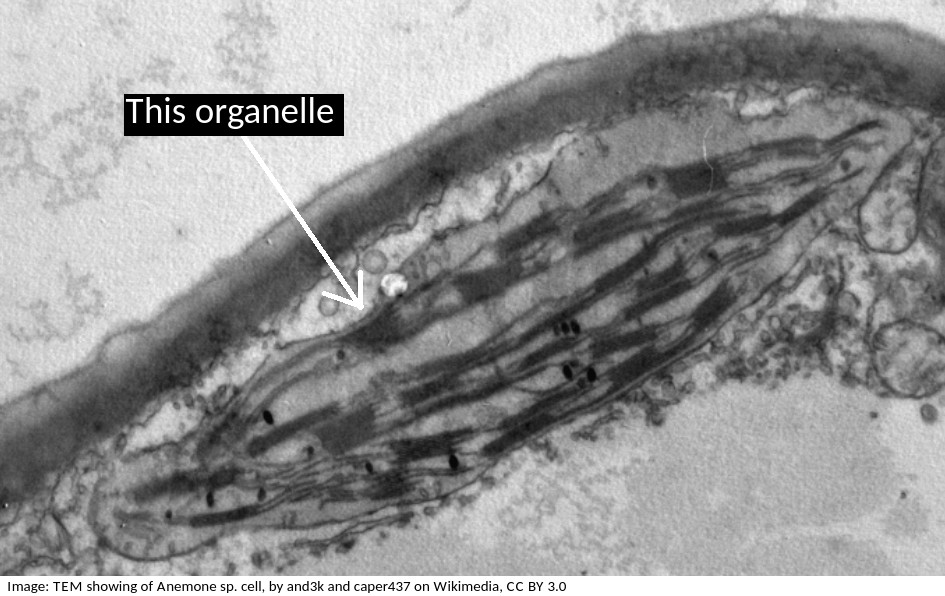
What is the name of the organelle?
Chloroplasts are distinctive because they have stacks of membranes inside, called grana, which hold the chlorophyll that absorbs light.
How does compartmentalisation by their internal membranes benefit eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryote cells (approx. 100µm in diameter) are much larger than prokaryote cells (approx 1µm) and so the concentration of reactants in the cytoplasm would be more dilute if all the metabolism happened in the cytoplasm.
Specialist organelles, like mitochondria keep the enzymes for aerobic respiration in one place, which increases their concentration, and increases the rate of reactions.
What is the importance of surface area to volume ratio to cells?
Surface area to volume ratio is important in the limitation of cell size. The lager the volume, the greater the need for materials which have to be exchanged over the surface of the cell.
The image below shows erythrocytes and leucocytes.l.
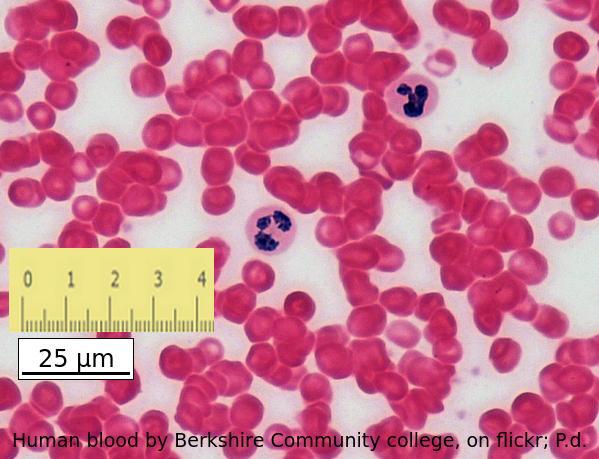
Using the scale bar and the ruler placed on the image, estimate the magnification of the image.
Which answer is the best estimate
Calculate the magnification of an electron microscope image from a scale bar?
Convert the ruler measurement to the same units written on the scale bar, in this case 25mm is 25000µm
then divide the ruler measurement 25000 by the number on the scalebar, 25.
The blood cells below were imaged using an electron microscope.
The magnification is x3000 and the ruler measures the central cell as being 2 cm in diameter.
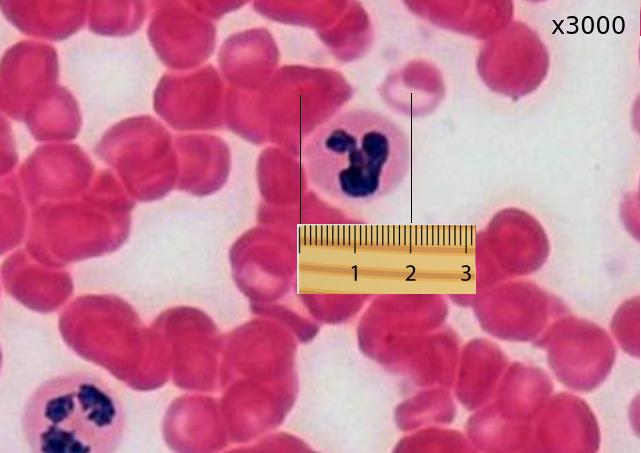
Estimate the actual size of this white blood cell.
Calculate specimen size using magnification?
First change the size measurement into µm units = 20000µm
Then divide by the magnification. 20000 / 3000 = 20 / 3 = 6.6 µm
The image below shows a eukaryotic cell.

Which structure, visible in the image, could be used as evidence supporting endosymbiosis?
The mitochondria provide evidence supporting endosymbiosis because they have:
- a double membrane
- 70S ribosomes
- DNA
Which of the following could be used to distinguish a living from a non- living object
Comment: Inanimate objects can move, produce and utilise energy but the process of respiration is exclusive to living systems
Human red blood cells are circular and 0.6 μm in diameter. A photograph of a red blood cell is shown as an illustration in a book with a diameter of 1.2mm. What is the magnification of the diagram?
Comment: Convert 1.2 mm into μm by multiplying x 1000 = 1200 μm (so that both units are the same). Then you can see that 0.6 x 2000 = 1200. Or use the formula Magnification = Image size/true size. If the photograph is larger than the cell, the magnification could not be 0.5x which would make it smaller. Eliminate obviously incorrect answers.
The image shows a cross section of trachea epithelium tissue. What is the best definition of a tissue?

A tissue may have one cell type or several and may have one or more functions. Tracheal epithelium has goblet cells to secrete mucus and columnar epithelial cells with cilia to remove contaminants and pathogens from the air and sweep them away from the lungs.
The image is of a channel protein. What is the function of a membrane channel protein?

Channel proteins are used for facilitated diffusion down the concentration gradient.
A mitotic index taken from this microphotograph only would not be regarded as valid. How can a valid count be made?

Which of the following are believed to be endosymbiotic structures involved in cell locomotion in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Flagellae are locomotory structures found in some Monera (bacteria), and some eukaryotic cells such as male gametes and Protoctista. Mitochondria are not found in prokaryotes. Pseudopodia are involved in locomotion but only in cells without an external wall. Fimbriae in bacteria allow for binding to a host or substrate, the same name is given to projections in the oviduct that aid movement of the ovum towards the uterus.
There are twenty complete cells in this microphotograph (with complete nuclear material). Estimate the number of complete cells in prophase of mitosis.

There are 3 complete cells in prophase (chromosomes visible in a nucleus..
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.

 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn