Topic 1: Cell biology 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about cell biology.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Cell biology revision resources
This page lists the understandings and skills expected for Topic 1 and links to the sub-topic pages which contain detailed revision notes, activities and past paper style questions. Great for revision.
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
Huntington's Disease (HD) is a brain disorder that affects a person's ability to talk, and move. HD is caused by a faulty protein. The job of the protein is to direct vesicles containing important molecules to the outside of the cell. The chemicals are released when the vesicle reaches the membrane.
What is the name given to the release of chemicals by a cell in this way?
This is a type of secretion, the vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane and its contents are released. This is called "exocytosis".
Pasteur's experiment with 'swan neck' flasks showed that a sterile nutrient medium exposed to the air would not show any signs of bacterial growth under his conditions.
What prevented the growth of bacteria?
Pasteur's famous experiments with swan neck flasks showed that broth kept in a flask where no dust could settle in the nutrient medium, and thus no living cells could get in, would not go mouldy.
This disproved the theory of spontaeous generation.
The 64 codons of mRNA code for the same amino acids in almost all species. A rare exception is found in Paramecium where one of the "stop codons" actually codes for the amino acid glutamine.
What does this suggest about the origin of cells?
The 64 codons in the genetic code give rise to the same amino acids in nearly all organisms, There is very little variaion. If the genetic code had evolved several times in the history off life, there would be many differences.
The electron microscope image below shows three organelles found in an animal cell.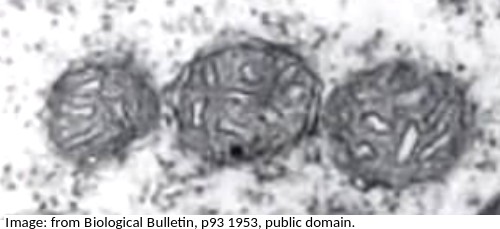
What is the name of the organelles?
Know how to idenfity the organelles in eukaryotes and draw their compartmentalised structure.
A mitochondrion (pleural = mitochondria) has an outer membrane and inner membrane folded into long thing 'flaps' called cristae.
The 'Cell theory' explains the nature of living things.
Which statement best describes Cell theory?
According to cell theory, living organisms are composed of cells.
Cells come from pre-existing cells and cells are the smallest using of life.
What is the importance of surface area to volume ratio to cells?
Surface area to volume ratio is important in the limitation of cell size. The lager the volume, the greater the need for materials which have to be exchanged over the surface of the cell.
The image below shows erythrocytes and leucocytes.l.
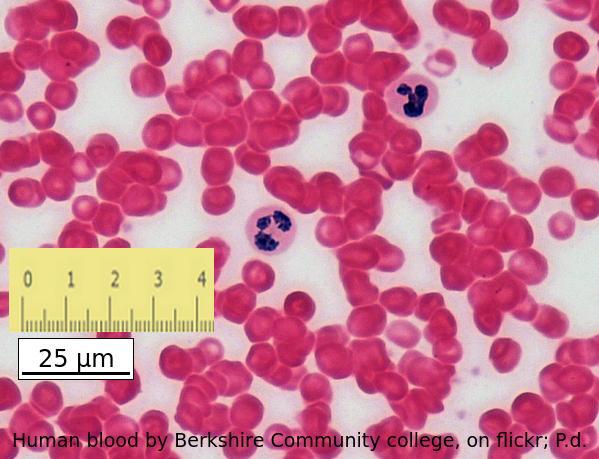
Using the scale bar and the ruler placed on the image, estimate the magnification of the image.
Which answer is the best estimate
Calculate the magnification of an electron microscope image from a scale bar?
Convert the ruler measurement to the same units written on the scale bar, in this case 25mm is 25000µm
then divide the ruler measurement 25000 by the number on the scalebar, 25.
If you know someone with a disease that might be cured by stem cell therapy then you might be a supporter of this research. You probably also know that some other people have deep concerns.
Which of the following is not a potential benefit of the use of stem cells?
There are ethical concerns about the use of embryo stem cells.
The research is expensive, and potential treatments are also likely to be expensive, and probably not available to all.
Many people who are against stem cells say that it is because cells are taken from human embryos, which have the potential for human live, and should be protected. There are other sources of stem cells, they argue.
Which of the following could be used to distinguish a living from a non- living object
Comment: Inanimate objects can move, produce and utilise energy but the process of respiration is exclusive to living systems
Which is the correct order of SI units, beginning with the largest?
Comment: SI units always have a differential of 1000. The unit without the prefix is the standard SI unit (metre, m). B and D are clearly wrong, eliminate those answers first.
The image is of a prokaryotic cell. Which feature defines the cell as prokaryotic?

The lack of a membrane bound nucleus (nucleoid) classifies a cell as prokaryotic.
The image shows a transverse section of a plant cell seen using an electron microscope.
What is the main function of the large organelle (A) seen in the cell?

The organelle shown is the nucleus, it stores the genetic information, DNA and is the location of DNA replication and Transcription.
The image is of a channel protein. What is the function of a membrane channel protein?

Channel proteins are used for facilitated diffusion down the concentration gradient.
Louis Pasteur used sterile broth and swan necked flasks to disprove which theory?

Pasteur demonstrated that broth would go cloudy only when air was allowed to contact the broth, bringing microbes. He disproved Spontaneous Generation.
A mitotic index taken from this microphotograph only would not be regarded as valid. How can a valid count be made?

Which property of stem cells is important for embryonic development?
Stem cells can divide and differentiate along different pathways. For a single fertilised egg cell to grow into an embryo both these processes are necessary.
What is the name of the process by which a white blood cell can engulf a pathogenic bacterium?
Endocytosis ("into the cell") is the process by which cells can engulf particles.
Which of the following are believed to be endosymbiotic structures involved in cell locomotion in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Flagellae are locomotory structures found in some Monera (bacteria), and some eukaryotic cells such as male gametes and Protoctista. Mitochondria are not found in prokaryotes. Pseudopodia are involved in locomotion but only in cells without an external wall. Fimbriae in bacteria allow for binding to a host or substrate, the same name is given to projections in the oviduct that aid movement of the ovum towards the uterus.
Why is the cell component in the image regarded as an organelle?

The organelle is a cell component with a membane, the mitochondrion, it is adapted to aerobic respiration.
The image below was taken in 1825 and shows part of the cell cycle.
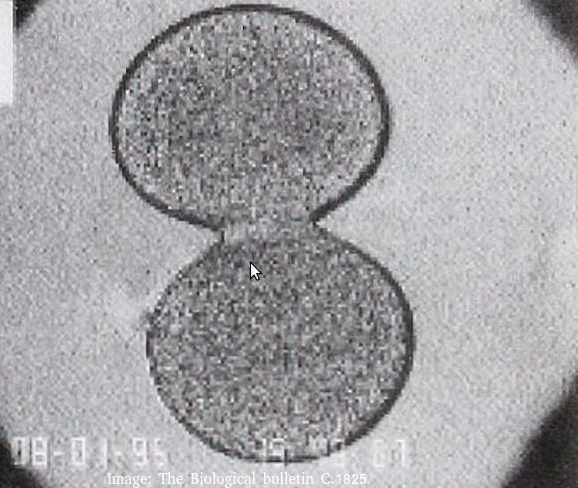
What is shown in the image?
Cytokinesis occurs after mitosis in plant and animal cells.
Animal cells form a cleavage furrow (looks like a wasps waist) as they don't have cell walls.
The two daughter cells are the same size, so cytokinesis is equal.
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.

 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn