Topic 1: Cell biology 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about cell biology.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Cell biology revision resources
This page lists the understandings and skills expected for Topic 1 and links to the sub-topic pages which contain detailed revision notes, activities and past paper style questions. Great for revision.
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
The image below shows a eukaryotic cell.
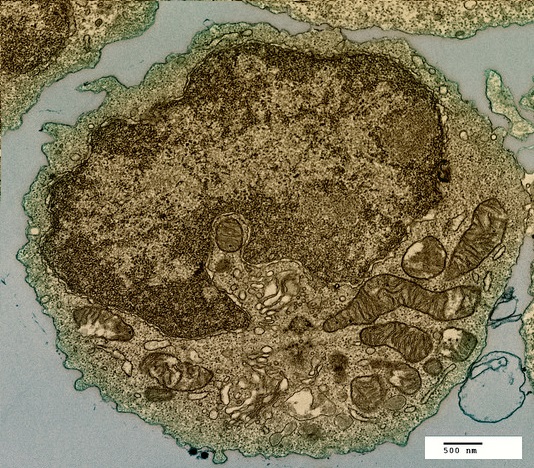
Which structure, visible in the image, could be used as evidence supporting endosymbiosis?
The mitochondria provide evidence supporting endosymbiosis because they have:
- a double membrane
- 70S ribosomes
- DNA
The DNA of eukaryote cells is organised into chromosomes
What happens to the DNA at prophase in the beginning of mitosis?
Chromosomes condense by supercoiling during mitosis. This makes the chromosomes visible.
The DNA replicates during interphase, not prophase.
The image below was taken in 1825 and shows part of the cell cycle.
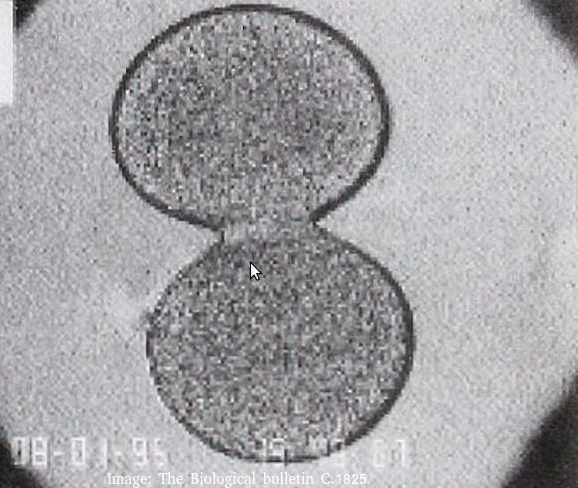
What type of cells is this and at which stage of the cell cycle?
Cytokinesis occurs after mitosis in plant and animal cells. The chromosomes are uncoiled.
Plant cells build a new cell wall which divides the cytoplasm.
Animal cells form a cleavage furrow (likes a wasps waist) as they don't have cell walls.
Which property of phospholipid molecules describes the fact that they have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts?
Phospholipids form bilayers in water due to the amphipathic properties of phospholipid molecules. The hydrophobic tails attract each other and the hydrophilic phosphates are attracted to the water.
Which of the following is true of peripheral proteins in cell membranes?
Membrane proteins are diverse in terms of structure, position in the membrane and function.
Peripheral proteins are attached to the membrane but found on its surface.
What are the structures labelled X and Y likely to be in this electron microscope image?
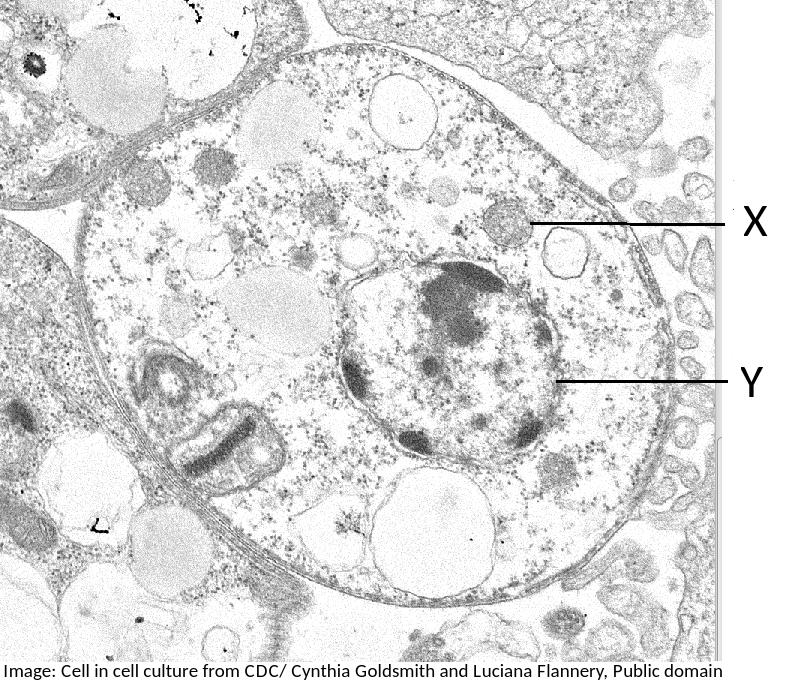
Students are expected to be able to identify organelles from microscope images of cells. The nucleus is distinctive because it is about 10µm in size, and it has black dots in it, chromatin, and sometimes one or more dark patches within the nuclear membrane. It also has a double membrane, not often easily visible.
If you found a eukaryote cell in an electron microscope image, and it contained a lot of rER, Golgi apparatus and many darkly stained vesicles, what do you think the function of the cell is most likely to be?
(eg. goblet cells which make mucus (a protien) will contain lots of rER and vesicles of musus, and palisade mesophyll cells which do photosynthesis will contain lots of chloroplasts)
The electron microscope image below shows a cell.
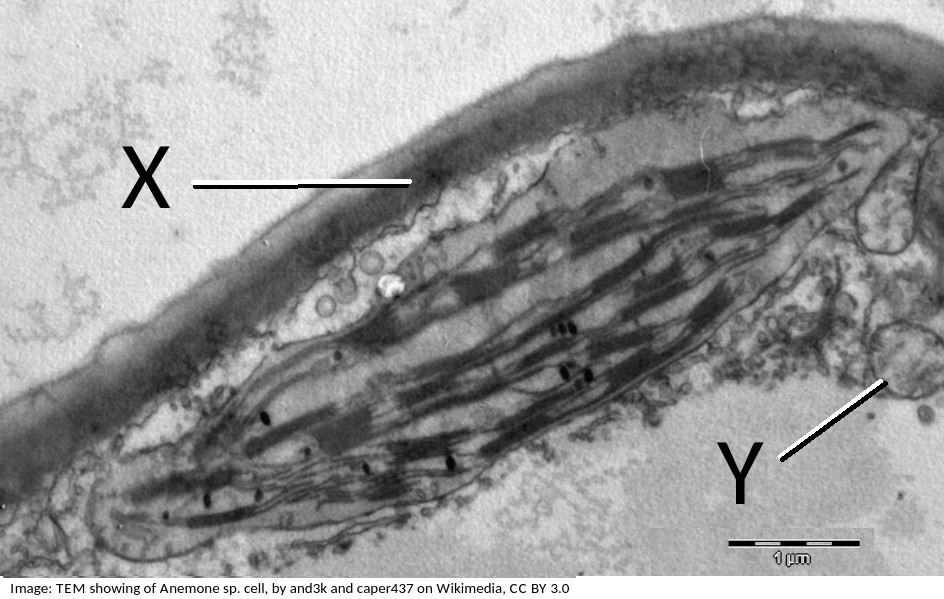
What are the organelles shown by the labels X & Y?
If you look closely at X, it points to the cell wall, outside the plasma membrane, it is close to the plasma membrane, but not touching the chloroplast.
The pale area below Y is the vacuole.
Organelle Y is a mitochondrion, you can tell this by its size, and the presence of membranes inside.
The electron microscope image below shows a scale bar marked with 100µm.
The large 'goblet cell' in the centre is producing mucous which will protect the surface of the epithelium.
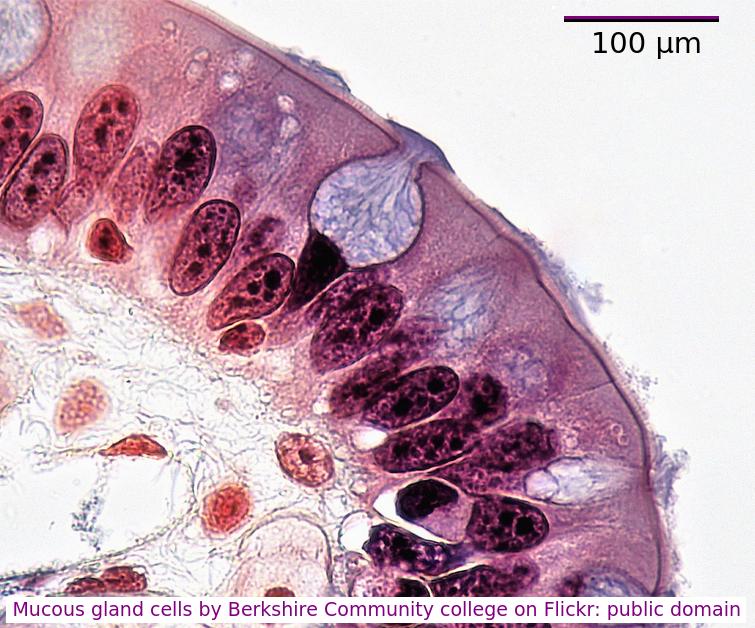
What is the diameter of the goblet cell?
Accurately, measure the scale bar length in mm, measure the diameter of the cell, in mm
divide cell diameter by scalebar and multiply by 100µm.
You can often estimate the size using the scale bar and your thumb or a pen.
The image below shows erythrocytes and leucocytes.l.
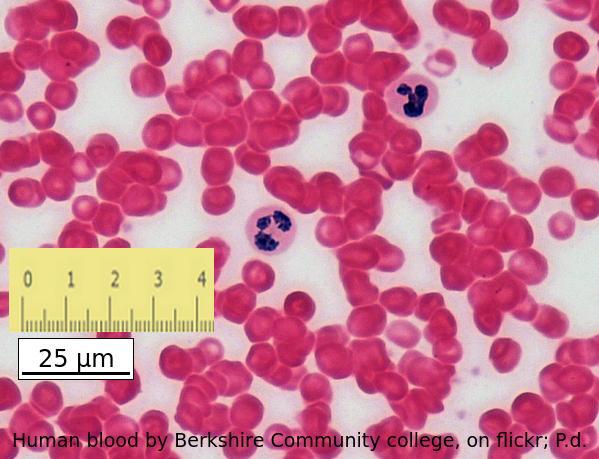
Using the scale bar and the ruler placed on the image, estimate the magnification of the image.
Which answer is the best estimate
Calculate the magnification of an electron microscope image from a scale bar?
Convert the ruler measurement to the same units written on the scale bar, in this case 25mm is 25000µm
then divide the ruler measurement 25000 by the number on the scalebar, 25.
Cells are often stored in isotonic conditions because they can be damaged in other concentrations, hypertonic, or hypotonic. Which of the descriptions of hypertonic is the most accurate?
Hypertonic solutions have a higher concentration of solutes, and lower water potentials than cells.
The diagram shows the transport of sodium ions across a membrane.
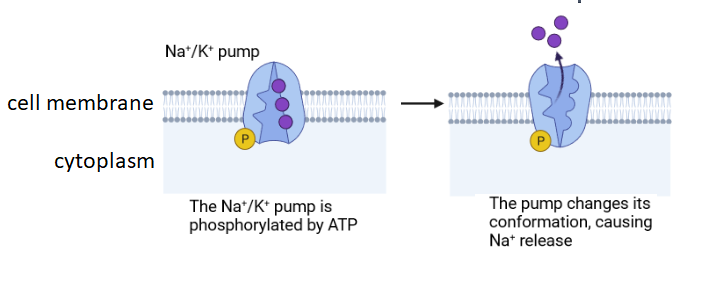
Which explanation gives the best description of the type of membrane transport shown?.
Facilitated diffusion does not require energy from ATP so this process is active transport. It can move sodium ions against the concentration gradient, but this is not always the case.
The image below shows a eukaryotic cell.

Which structure, visible in the image, could be used as evidence supporting endosymbiosis?
The mitochondria provide evidence supporting endosymbiosis because they have:
- a double membrane
- 70S ribosomes
- DNA
The image below is of Dracaena leaf upper epidermis cells.
Which of the following is the best estimate of the length (from top to bottom) of an epidermal cell?
Comment: The cells are approximately the same size as the scale bar.
This would make 70µm the closest estimate.
Which of the following are methods by which molecules can move across membranes?
I. Simple diffusion
II. Facilitated diffusion
III. Cytokinesis
IV. Active transport
There are actually four types of membrane transport which are required in DP Biology, Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis and active transport.
The diagram shows a typical eukaryotic plant cell. Which organelles are involved in supporting the cell and plant? I Cell wall II Cytoplasm III Nucleus IV Vacuole.

The cell and plant are supported by the turgor pressure of water in the vacuole acting on the rigid cell wall.
Which organelles are found in large numbers in secretory cells in animals? I Vesicles II Golgi Body III Mitochondria IV Rough endoplasmic reticulum.

Secretory cells synthesise proteins for exocytosis so have large numbers of mitochondria to supply energy, RER to synthesise the proteins for packaging into vesicles by the Golgi Body.
Protein channels cross the membrane to allow hydrophilic substances to pass through the membrane.
Which process is involved in white blood cells engulfing bacteria (arrowed in the photomicrograph)?

White blood cells engulf bacteria by endocytosis, the intake of solid particles by a cell membrane.
Which of the following is the best description of an organelle?
The "wrong" answers are correct statements but are distractors, not the best description.
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.


 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn