Topic 1: Cell biology 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about cell biology.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Cell biology revision resources
This page lists the understandings and skills expected for Topic 1 and links to the sub-topic pages which contain detailed revision notes, activities and past paper style questions. Great for revision.
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
The 64 codons of mRNA code for the same amino acids in almost all species. A rare exception is found in Paramecium where one of the "stop codons" actually codes for the amino acid glutamine.
What does this suggest about the origin of cells?
The 64 codons in the genetic code give rise to the same amino acids in nearly all organisms, There is very little variaion. If the genetic code had evolved several times in the history off life, there would be many differences.
The image below was taken in 1825 and shows part of the cell cycle.
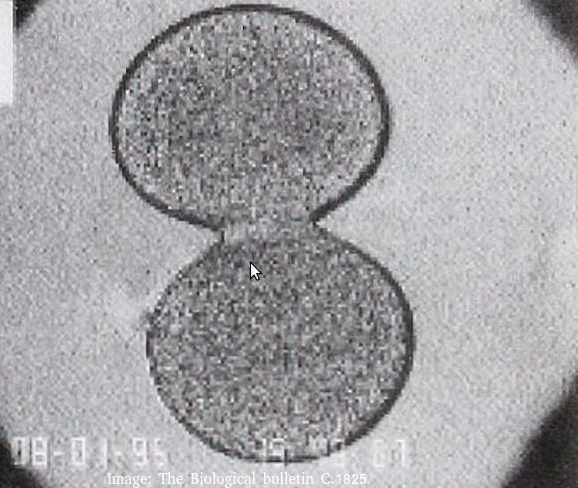
What type of cells is this and at which stage of the cell cycle?
Cytokinesis occurs after mitosis in plant and animal cells. The chromosomes are uncoiled.
Plant cells build a new cell wall which divides the cytoplasm.
Animal cells form a cleavage furrow (likes a wasps waist) as they don't have cell walls.
The four cells shown below have each been surrounded by a solution for 1 hour.
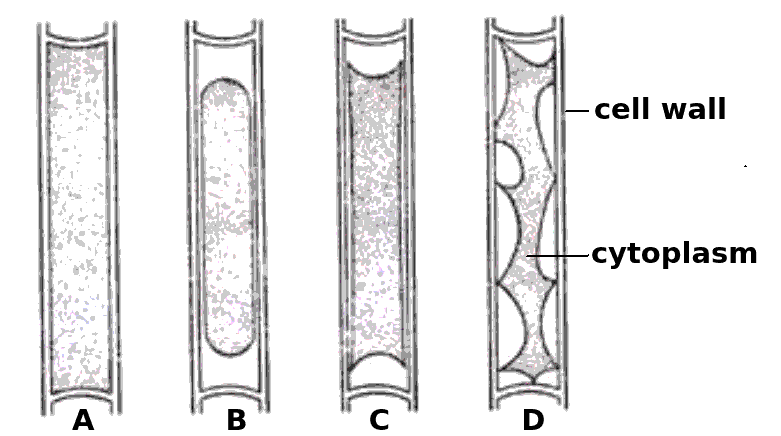
Which cells have been in a hypertonic solution ?
Cell A is swollen turgid, it is in a hypotonic solution or an isotonic solution.
The cells B, C and D show increasing signs of plasmolysis, and so they must be in hypertonic solutions.
Skill: Estimation of osmolarity in tissues by bathing samples in hypotonic and hypertonic solutions. (Practical 2)
The graph below shows the % change in mass of carrot parenchyma slices at different concentrations of sucrose.
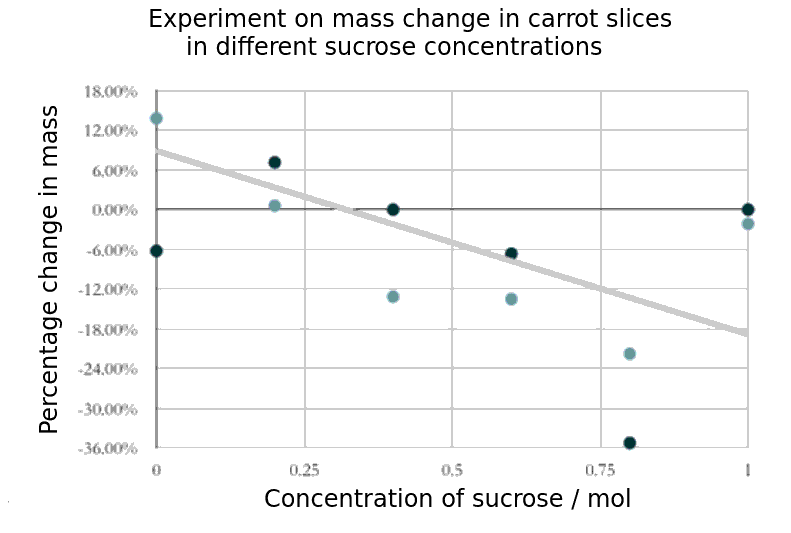
Which of the following is the best estimate of the molarity of the cytoplasm of these cells?
When a sample of cells show no change in mass, then the net movement of water by osmosis must be zero. This shows the concentration of the cytoplasm of the cells. In this graph it would be about 0.3 mol
The electron microscope image below shows an organelle found in both animal and plant cells.

What is the name of the organelle?
Know how to idenfity the organelles in eukaryotes and draw their compartmentalised structure.
The rER has parallel membranes covered in dots, which are ribosomes, used for making proteins, for secretion from the cell.
How does compartmentalisation by their internal membranes benefit eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryote cells (approx. 100µm in diameter) are much larger than prokaryote cells (approx 1µm) and so the concentration of reactants in the cytoplasm would be more dilute if all the metabolism happened in the cytoplasm.
Specialist organelles, like mitochondria keep the enzymes for aerobic respiration in one place, which increases their concentration, and increases the rate of reactions.
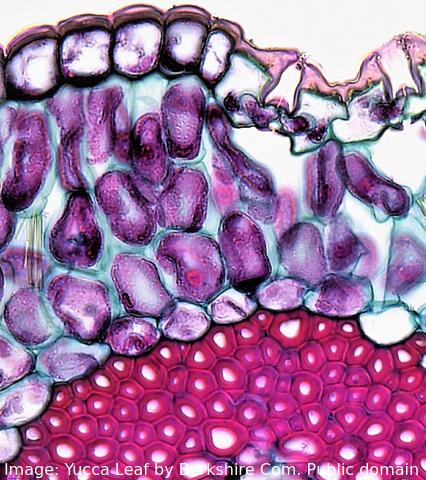 The image shows a range of different cell types in the leaf of a Yucca plant.
The image shows a range of different cell types in the leaf of a Yucca plant.
How do stem cells form this range of cells?
What is the process called?
Specialised tissues can develop by cell differentiation in multicellular organisms.
Differentiation involves the expression of some genes and not others in a cell.
The blood cells below were imaged using an electron microscope.
The magnification is x3000 and the ruler measures the central cell as being 2 cm in diameter.
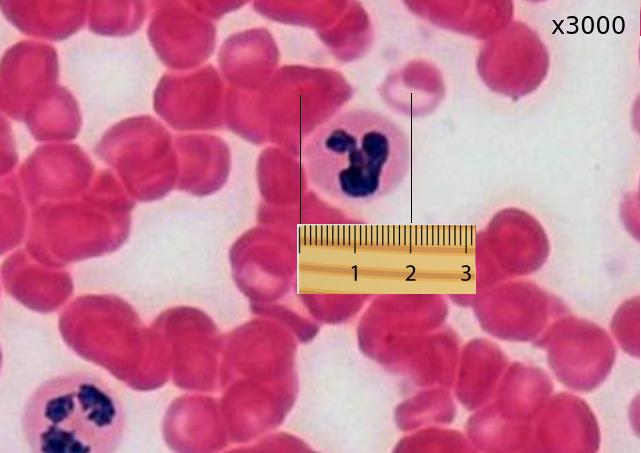
Estimate the actual size of this white blood cell.
Calculate specimen size using magnification?
First change the size measurement into µm units = 20000µm
Then divide by the magnification. 20000 / 3000 = 20 / 3 = 6.6 µm
Which of the structures listed below are involved in membrane transport?
Many transmembrane proteins are involved in transport of molecules across membranes. These can either provide a sort of molecular pore through which ions or molecules can pass (facilitated diffusion), or they can use ATP to actively move molecules, even against the concentration gradient (active transport).These are just two examples, transport can also occur by simple diffusion through the phospholipid bilayer, or by endocytosis.
Cells are often stored in isotonic conditions because they can be damaged in other concentrations, hypertonic, or hypotonic. Which of the descriptions of hypertonic is the most accurate?
Hypertonic solutions have a higher concentration of solutes, and lower water potentials than cells.
Which phrases most accurately describe a multicellular organism?
Comment: The multicellular condition allows for differentiation into cells of different types and also replacement of cells when injured or damaged.
Why is a fungal hypha an exception to the cell theory?

A fungal hypha has many nuclei in a hypha but no cross walls to divide the hypha into cells.
The microphotograph is of stratified epithelium. Cells are produced by mitosis in the area marked 1 and eventually reach the surface to replace lost cells. Which biological processes does this represent?

The cells produced by mitosis differentiate into mature cells and replace the cells lost at the surface.
The image is a ribbon model of a channel protein. Where would this be found in a plasma membrane?

Channel proteins penetrate the membrane and have a central hydrophilic area (yellow in the diagram which is shown from above).
What is the sequence of events that occur in a cell that is secreting a protein hormone?
1 Exocytosis
2 Vesicle formed by Golgi Body
3 Fusion of vesicle to plasma membrane
4 RER manufactures protein.
Ribosomes on the RER manufacture protein. This is packaged in vesicles by the Golgi Body and moves to the surface of the cell where the vesicle and plasma membrane fuse and exocytosis of the protein occurs.
The theory of spontaneous generation has been disproved by Pasteur's experiment. Is there a point in evolution when spontaneous generation did occur?
The first cells must have arisen spontaneously from non-living matter, probably in volcanic vents, but the universal nature of cell ultrastructure and of the genetic code makes it likely that this only happened once.
Which of the following contributed to the acceptance of the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure of Singer and Nicholson in place of the original Davison-Danielli model?
I Hydrophobic membrane proteins
II Irregular sizes of membrane proteins
III Increased magnification of light microscopes.
IV Fluorescent antibody tagging.
The irregular sizes and insolubility of hydrophobic membrane proteins indicated that they could not be a surface layer as proposed by Davison-Danielli. This was confirmed by fluoresecent antibodies showing that proteins were both within and on the membrane.
Why is the cell component in the image regarded as an organelle?

The organelle is a cell component with a membane, the mitochondrion, it is adapted to aerobic respiration.
There are twenty complete cells in this microphotograph (with complete nuclear material). Estimate the number of complete cells in prophase of mitosis.

There are 3 complete cells in prophase (chromosomes visible in a nucleus..
A tissue is placed in an isotonic solution. Which of the following is the best description of water movement between the tissue and the solution?
There is no net water movement, gain and loss from the tissue is equal in both directions.
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.

 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn