Topic 1: Cell biology 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about cell biology.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Cell biology revision resources
This page lists the understandings and skills expected for Topic 1 and links to the sub-topic pages which contain detailed revision notes, activities and past paper style questions. Great for revision.
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
The 64 codons in the genetic code give rise to the same amino acids in nearly all organisms.
There is very little variaion. This is evidence for a single common origin of life.
Differences in the frequency of amino acid use reflects the different genes in the two organisms.
During interphase of the cell cycle what happens to the DNA in the nucleus?
Under the microscope there is little change during interphase.
However interphase is a very active phase of the cell cycle with many processes occurring in the nucleus and cytoplasm. (It is subdivided into G1, S, G2 phases of the cell cycle)
DNA replication occurs during the S-phase.
Which one of the statements below best describes the mitotic index?
The mitotic shows the speed of cell division, which can be used as a tool to identify cancer.
It is calculated by dividing the number of cells doing mitosis by the total number of cells.
Sodium channels are made from a protein.
Where in the cell are sodium channel proteins found?
Sodium channel proteins are found spanning the plasma membrane. Their structure helps the function for facilitated diffusion in cells because they allow ions to pass cross the membrane.
If the protein was not a trans-membrane protein then it would not be able to transport ions across the membrane.
This box contains a lung waiting for a transplant operation.
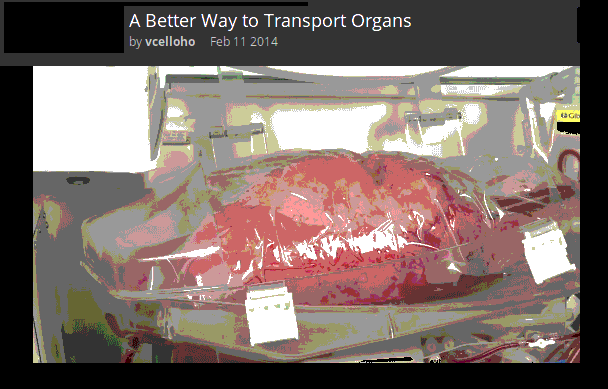
What is special about the solution inside the box which surrounds the tissue?
Tissues and organs must be kept in a solution with the same osmolarity as the cytoplasm of the cells to prevent osmosis. If they were kept in pure water, osmosis would carry water into the cells and they would burst, causing damage to the cells. If the solution was hypertonic, the tissue would lose water (and gain ions).
The four cells shown below have each been surrounded by a solution for 1 hour.
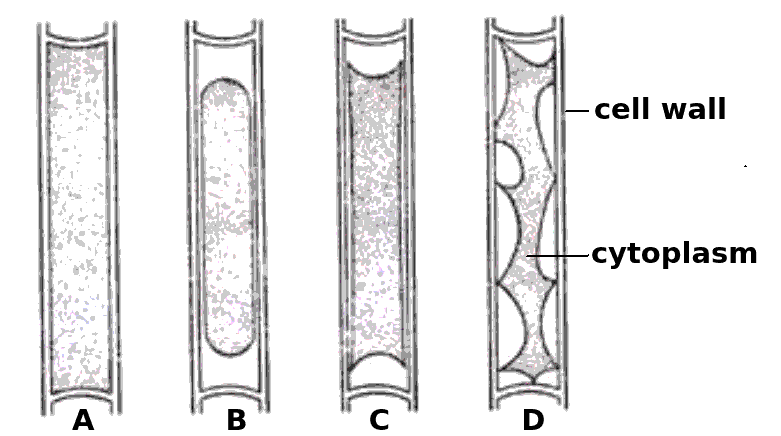
Which cells have been in a hypertonic solution ?
Cell A is swollen turgid, it is in a hypotonic solution or an isotonic solution.
The cells B, C and D show increasing signs of plasmolysis, and so they must be in hypertonic solutions.
Skill: Estimation of osmolarity in tissues by bathing samples in hypotonic and hypertonic solutions. (Practical 2)
Which property of phospholipid molecules describes the fact that they have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts?
Phospholipids form bilayers in water due to the amphipathic properties of phospholipid molecules. The hydrophobic tails attract each other and the hydrophilic phosphates are attracted to the water.
The electron microscope image below shows an organelle found in both animal and plant cells.

What is the name of the organelle?
Know how to idenfity the organelles in eukaryotes and draw their compartmentalised structure.
The rER has parallel membranes covered in dots, which are ribosomes, used for making proteins, for secretion from the cell.
The electron microscope image below shows a ciliated epithelial cell from the trachea.
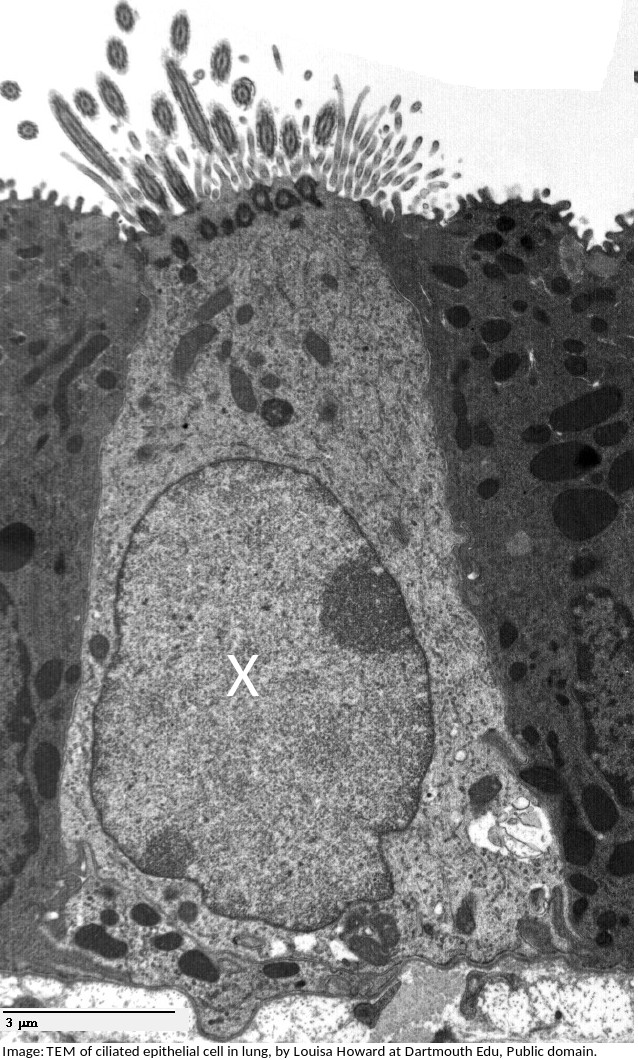
What is the name of the organelle labelled X?
How does compartmentalisation by their internal membranes benefit eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryote cells (approx. 100µm in diameter) are much larger than prokaryote cells (approx 1µm) and so the concentration of reactants in the cytoplasm would be more dilute if all the metabolism happened in the cytoplasm.
Specialist organelles, like mitochondria keep the enzymes for aerobic respiration in one place, which increases their concentration, and increases the rate of reactions.
What is the importance of surface area to volume ratio to cells?
Surface area to volume ratio is important in the limitation of cell size. The lager the volume, the greater the need for materials which have to be exchanged over the surface of the cell.
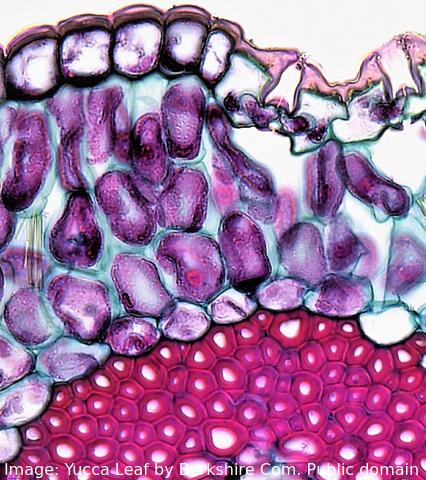 The image shows a range of different cell types in the leaf of a Yucca plant.
The image shows a range of different cell types in the leaf of a Yucca plant.
How do stem cells form this range of cells?
What is the process called?
Specialised tissues can develop by cell differentiation in multicellular organisms.
Differentiation involves the expression of some genes and not others in a cell.
Stargardts disease is vision loss caused by the death of both cone cells and rod cells in the part of the retina around the fovea. One potential treatment for Stargardts disease is the use of human embryonic stem cells.
What are the properties of these stem cells, which other cells don't have, that makes them so useful for this treatment?
Stem cells can divide and this help researchers to grow them in the lab.
They can differentiate along different pathways in embryonic development which makes stem cells useful for therapeutic uses (e.g. Stargart's disease) because they can be grown into many different tissues.
Cells are often stored in isotonic conditions because they can be damaged in other concentrations, hypertonic, or hypotonic. Which of the descriptions of hypertonic is the most accurate?
Hypertonic solutions have a higher concentration of solutes, and lower water potentials than cells.
Which label in the image below shows the process of endocytosis?
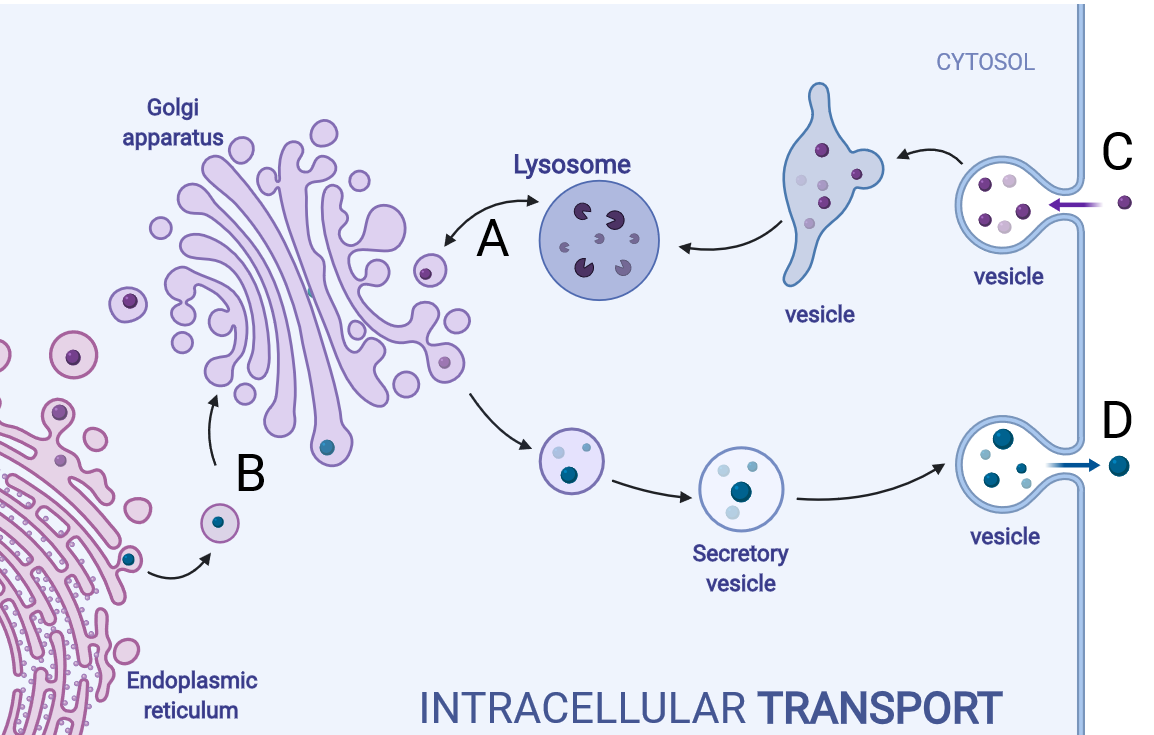
Endocytosis is the process where a substance is surrounded by the plasma membrane which forms a vesicle inside the cell that then moves into the cytoplasm, separating from the plasma membrane.
Which two processes are involved in cell differentiation?
Comment: During differentiation genes may be activated or repressed causing the formation of different proteins by the ribosomes but other organelles such as mitochondria continue to function in the same way
What best describes the organism in the light microscope image?

It is unicellular (one cell) and a eukaryote (has a nucleus) and not autotrophic.
What is the approximate length of the bacterial cell in the image?

The scale bar is 1 µm and the bacterium is approximately 3 times the length of the scale bar.
Which organelles are found in large numbers in secretory cells in animals? I Vesicles II Golgi Body III Mitochondria IV Rough endoplasmic reticulum.

Secretory cells synthesise proteins for exocytosis so have large numbers of mitochondria to supply energy, RER to synthesise the proteins for packaging into vesicles by the Golgi Body.
Which process is involved in white blood cells engulfing bacteria (arrowed in the photomicrograph)?

White blood cells engulf bacteria by endocytosis, the intake of solid particles by a cell membrane.
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.

 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn