Topic 1: Cell biology 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about cell biology.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Cell biology revision resources
This page lists the understandings and skills expected for Topic 1 and links to the sub-topic pages which contain detailed revision notes, activities and past paper style questions. Great for revision.
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
Huntington's Disease (HD) is a brain disorder that affects a person's ability to talk, and move. HD is caused by a faulty protein. The job of the protein is to direct vesicles containing important molecules to the outside of the cell. The chemicals are released when the vesicle reaches the membrane.
What is the name given to the release of chemicals by a cell in this way?
This is a type of secretion, the vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane and its contents are released. This is called "exocytosis".
Spontaneous generation was a popular concept a few hundred years ago.
Which of the following statements best summarises the theory?
The theory of spontaneous generation tried to explain the occurance of organisms like maggots, mould and bacteria in rotting food. Pasteur's experiments falsified this theory.
During interphase of the cell cycle what happens to the DNA in the nucleus?
Under the microscope there is little change during interphase.
However interphase is a very active phase of the cell cycle with many processes occurring in the nucleus and cytoplasm. (It is subdivided into G1, S, G2 phases of the cell cycle)
DNA replication occurs during the S-phase.
Which of the following is true of peripheral proteins in cell membranes?
Membrane proteins are diverse in terms of structure, position in the membrane and function.
Peripheral proteins are attached to the membrane but found on its surface.
The electron microscope image below shows an organelle found in both animal and plant cells.

What is the name of the organelle?
Know how to idenfity the organelles in eukaryotes and draw their compartmentalised structure.
The rER has parallel membranes covered in dots, which are ribosomes, used for making proteins, for secretion from the cell.
The electron microscope image below shows an organelle found in eukaryote cells.
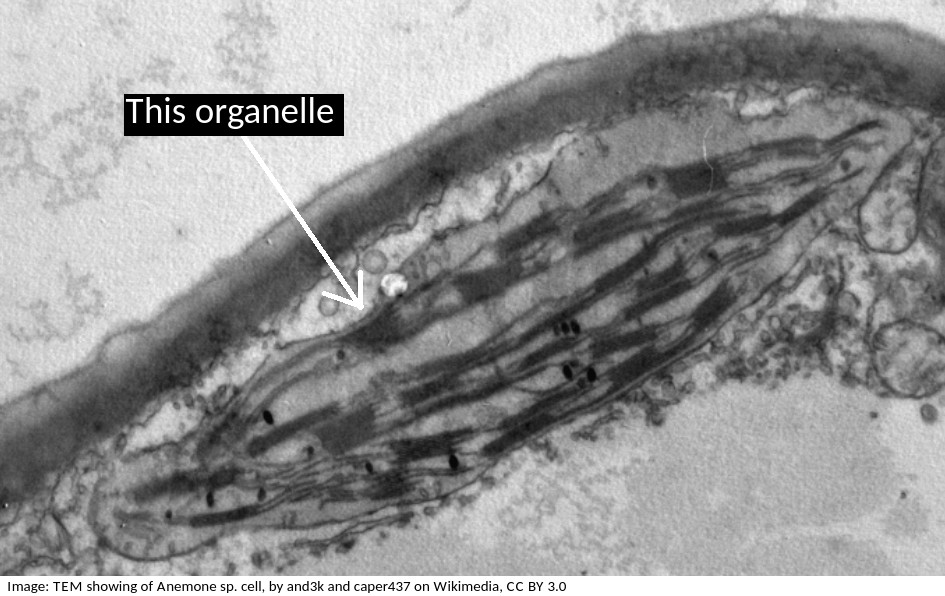
What is the name of the organelle?
Chloroplasts are distinctive because they have stacks of membranes inside, called grana, which hold the chlorophyll that absorbs light.
The electron microscope image below shows a cell.
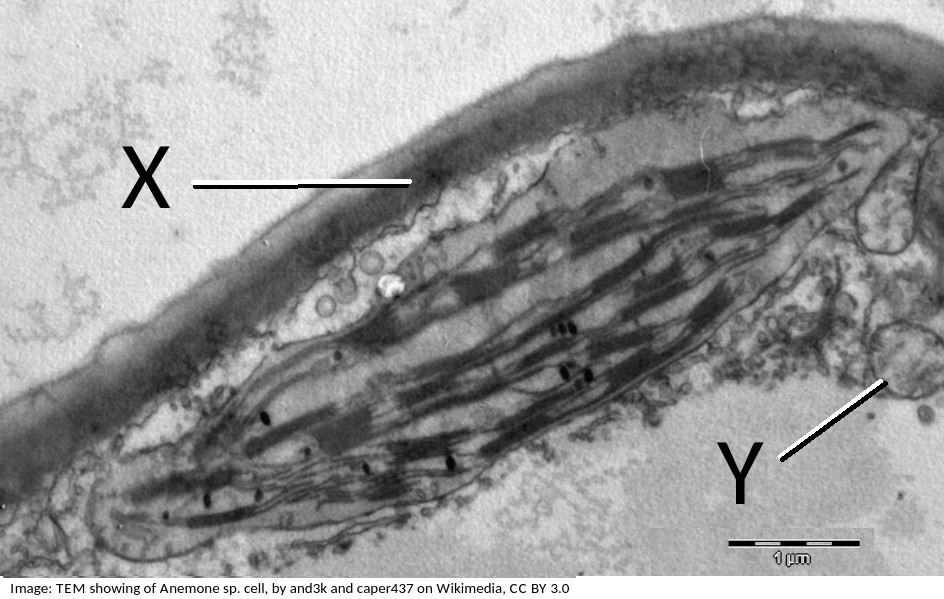
What are the organelles shown by the labels X & Y?
If you look closely at X, it points to the cell wall, outside the plasma membrane, it is close to the plasma membrane, but not touching the chloroplast.
The pale area below Y is the vacuole.
Organelle Y is a mitochondrion, you can tell this by its size, and the presence of membranes inside.
What is the term used to describe the smallest distance which two objects can be seen as separate objects in a microscope?
The resolving power, or resolution, is the ability to separate objects, to produce separate images of two objects.
Cell theory covers most, but not all cases.
Which one of these statements is an exception?
Exceptions to cell theory are : multinucleated striated muscle the giant single celled Acetabularia algae?
Also, organisms consisting of only one cell carry out all functions of life in that cell. e.g. Paramecium, Chlorella.
When nerve cells form brain tissue they can; store memories, create thoughts and coordinate movement.
If you only ever studied individual nerve cells you would never see these abilities which the brain has.
What is this type of property called?
Multicellular organisms have properties that emerge from the interaction of their cellular components. (Emergent properties)
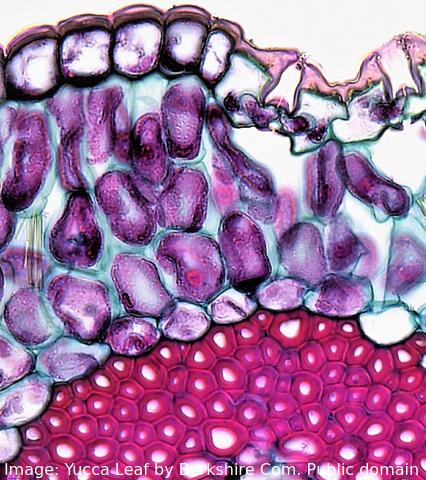 The image shows a range of different cell types in the leaf of a Yucca plant.
The image shows a range of different cell types in the leaf of a Yucca plant.
How do stem cells form this range of cells?
What is the process called?
Specialised tissues can develop by cell differentiation in multicellular organisms.
Differentiation involves the expression of some genes and not others in a cell.
Which of the structures listed below are involved in membrane transport?
Many transmembrane proteins are involved in transport of molecules across membranes. These can either provide a sort of molecular pore through which ions or molecules can pass (facilitated diffusion), or they can use ATP to actively move molecules, even against the concentration gradient (active transport).These are just two examples, transport can also occur by simple diffusion through the phospholipid bilayer, or by endocytosis.
Which label in the image below shows the process of endocytosis?
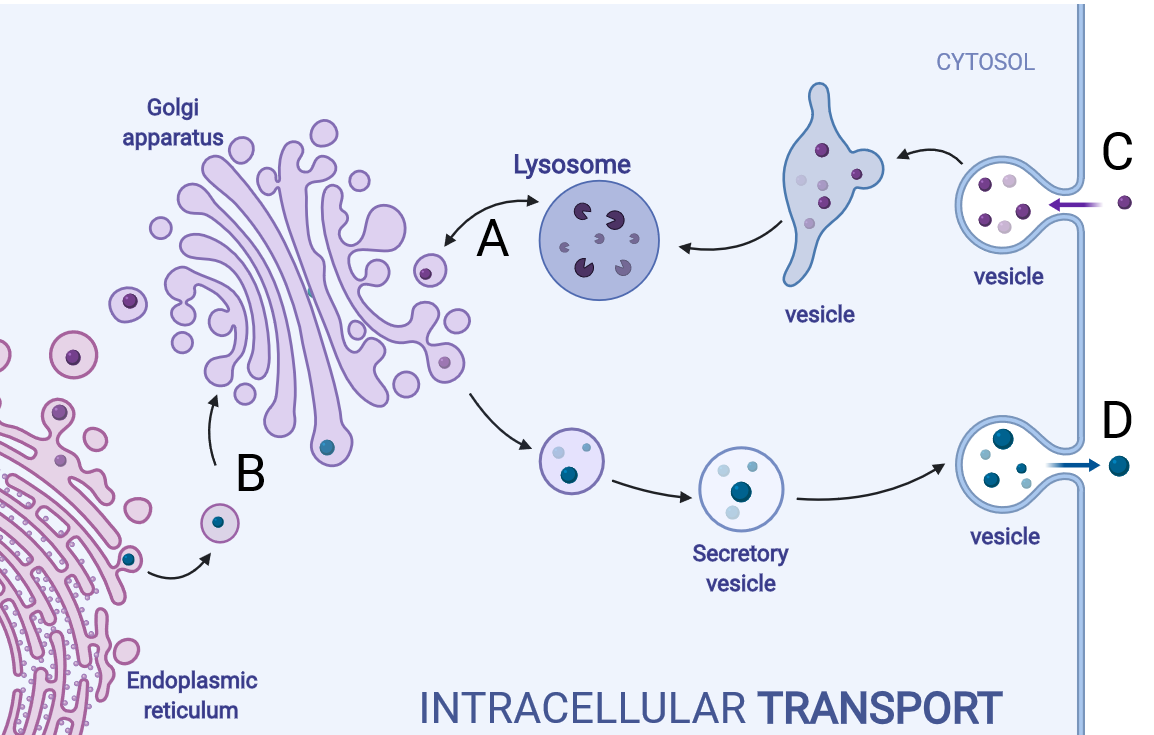
Endocytosis is the process where a substance is surrounded by the plasma membrane which forms a vesicle inside the cell that then moves into the cytoplasm, separating from the plasma membrane.
The image below shows a eukaryotic cell.
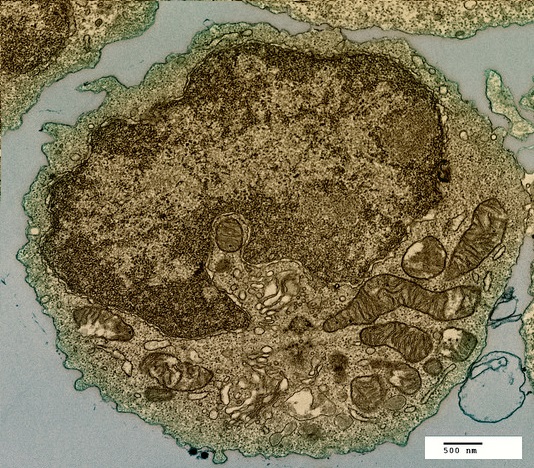
Which structure, visible in the image, could be used as evidence supporting endosymbiosis?
The mitochondria provide evidence supporting endosymbiosis because they have:
- a double membrane
- 70S ribosomes
- DNA
Human red blood cells are circular and 0.6 μm in diameter. A photograph of a red blood cell is shown as an illustration in a book with a diameter of 1.2mm. What is the magnification of the diagram?
Comment: Convert 1.2 mm into μm by multiplying x 1000 = 1200 μm (so that both units are the same). Then you can see that 0.6 x 2000 = 1200. Or use the formula Magnification = Image size/true size. If the photograph is larger than the cell, the magnification could not be 0.5x which would make it smaller. Eliminate obviously incorrect answers.
Which of the following are methods by which molecules can move across membranes?
I. Simple diffusion
II. Facilitated diffusion
III. Cytokinesis
IV. Active transport
There are actually four types of membrane transport which are required in DP Biology, Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis and active transport.
The image is of a prokaryotic cell. Which feature defines the cell as prokaryotic?

The lack of a membrane bound nucleus (nucleoid) classifies a cell as prokaryotic.
The image is of a channel protein. What is the function of a membrane channel protein?

Channel proteins are used for facilitated diffusion down the concentration gradient.
What tonicity should a saline drip have in comparison to human blood?

The saline drip must be isotonic to human blood to not cause water gain or loss from tissues.
Which of the following contributed to the acceptance of the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure of Singer and Nicholson in place of the original Davison-Danielli model?
I Hydrophobic membrane proteins
II Irregular sizes of membrane proteins
III Increased magnification of light microscopes.
IV Fluorescent antibody tagging.
The irregular sizes and insolubility of hydrophobic membrane proteins indicated that they could not be a surface layer as proposed by Davison-Danielli. This was confirmed by fluoresecent antibodies showing that proteins were both within and on the membrane.
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.

 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn