Topic 1: Cell biology 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about cell biology.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Cell biology revision resources
This page lists the understandings and skills expected for Topic 1 and links to the sub-topic pages which contain detailed revision notes, activities and past paper style questions. Great for revision.
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
Which cells are produced when a diploid cell divides by mitosis?
Mitosis is division of the nucleus into two genetically identical daughter nuclei in eukaryote cells.
A diploid cell will produce two diploid daughter cells in one division of mitosis.
The four cells shown below have each been surrounded by a solution for 1 hour.
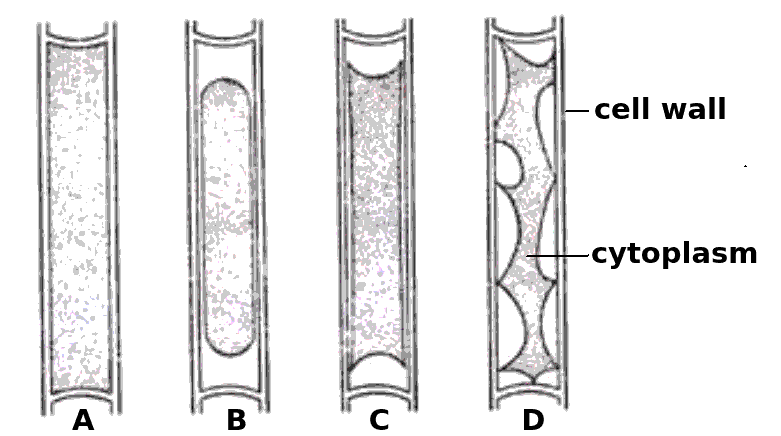
Which cells have been in a hypertonic solution ?
Cell A is swollen turgid, it is in a hypotonic solution or an isotonic solution.
The cells B, C and D show increasing signs of plasmolysis, and so they must be in hypertonic solutions.
Skill: Estimation of osmolarity in tissues by bathing samples in hypotonic and hypertonic solutions. (Practical 2)
The illustration shown below is of a protein (green) attached to a membrane.
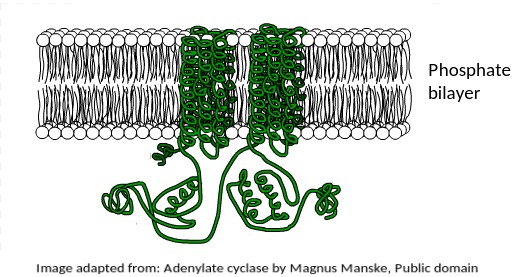
What is the most likely function of this membrane protein?
This protein is found in the human liver, where the hormone adrenaline indirectly stimulates it to mobilise stored energy inside liver cells in the "fight or flight" response.
The fact that it is a transmembrane protein is essential for this function.
It is interesting to note that this protein is also secreted by Anthrax bacteria as a toxin.
It upsets the metabolism of host cells when it enters them.
The electron microscope image below shows an organelle found in eukaryote cells.
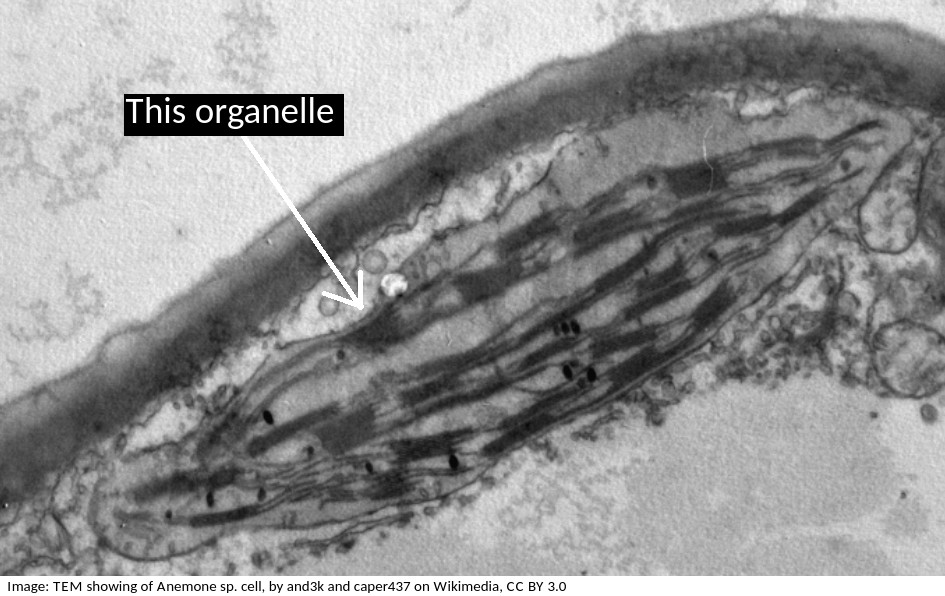
What is the name of the organelle?
Chloroplasts are distinctive because they have stacks of membranes inside, called grana, which hold the chlorophyll that absorbs light.
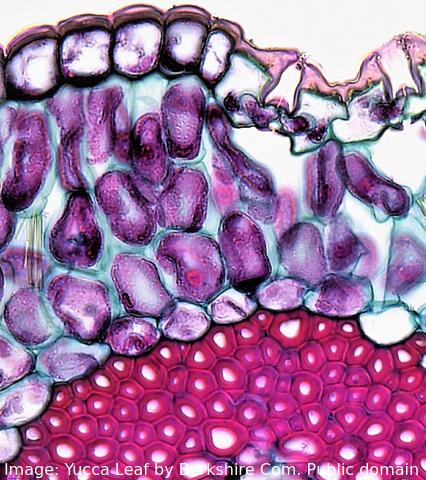 The image shows a range of different cell types in the leaf of a Yucca plant.
The image shows a range of different cell types in the leaf of a Yucca plant.
How do stem cells form this range of cells?
What is the process called?
Specialised tissues can develop by cell differentiation in multicellular organisms.
Differentiation involves the expression of some genes and not others in a cell.
Which phrases most accurately describe a multicellular organism?
Comment: The multicellular condition allows for differentiation into cells of different types and also replacement of cells when injured or damaged.
Which is the best definition of a tissue?
Comment:Tissues may have one or several cell types and one or more functions
Which of the following could be used to distinguish a living from a non- living object
Comment: Inanimate objects can move, produce and utilise energy but the process of respiration is exclusive to living systems
The image shows a cross section of trachea epithelium tissue. What is the best definition of a tissue?

A tissue may have one cell type or several and may have one or more functions. Tracheal epithelium has goblet cells to secrete mucus and columnar epithelial cells with cilia to remove contaminants and pathogens from the air and sweep them away from the lungs.
What best describes the organism in the light microscope image?

It is unicellular (one cell) and a eukaryote (has a nucleus) and not autotrophic.
The diagram shows a typical eukaryotic plant cell. Which organelles are involved in supporting the cell and plant? I Cell wall II Cytoplasm III Nucleus IV Vacuole.

The cell and plant are supported by the turgor pressure of water in the vacuole acting on the rigid cell wall.
The image is of a prokaryotic cell. Which feature defines the cell as prokaryotic?

The lack of a membrane bound nucleus (nucleoid) classifies a cell as prokaryotic.
The image shows a transverse section of a plant cell seen using an electron microscope.
What is the main function of the large organelle (A) seen in the cell?

The organelle shown is the nucleus, it stores the genetic information, DNA and is the location of DNA replication and Transcription.
The image is a ribbon model of a channel protein. Where would this be found in a plasma membrane?

Channel proteins penetrate the membrane and have a central hydrophilic area (yellow in the diagram which is shown from above).
What is the sequence of events that occur in a cell that is secreting a protein hormone?
1 Exocytosis
2 Vesicle formed by Golgi Body
3 Fusion of vesicle to plasma membrane
4 RER manufactures protein.
Ribosomes on the RER manufacture protein. This is packaged in vesicles by the Golgi Body and moves to the surface of the cell where the vesicle and plasma membrane fuse and exocytosis of the protein occurs.
Which organelles in a plant cell are believed to have originated as free-living prokaryotic cells?

Both the mitochondria and the chloroplast in plant cells are thought to have been free-living prokaryotes which evolved in a symbiotic relationship with a eukaryotic cell.
Which is the best description of the genetic code?
The genetic code is universal (the codons code for the same amino acid in all organisms) but there are a very few exceptions, mostly in Archaea. A mutation does not alter the genetic code, it alters the base sequence of DNA.
What is the structure of the genetic material found in a mitochondrion?
Mitochondrial DNA is a single helical molecule, not associated with protein and circular in shape. The same as prokaryote nucleoid DNA.
The theory of spontaneous generation has been disproved by Pasteur's experiment. Is there a point in evolution when spontaneous generation did occur?
The first cells must have arisen spontaneously from non-living matter, probably in volcanic vents, but the universal nature of cell ultrastructure and of the genetic code makes it likely that this only happened once.
Which of the following contributed to the acceptance of the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure of Singer and Nicholson in place of the original Davison-Danielli model?
I Hydrophobic membrane proteins
II Irregular sizes of membrane proteins
III Increased magnification of light microscopes.
IV Fluorescent antibody tagging.
The irregular sizes and insolubility of hydrophobic membrane proteins indicated that they could not be a surface layer as proposed by Davison-Danielli. This was confirmed by fluoresecent antibodies showing that proteins were both within and on the membrane.
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.

 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn