Topic 1: Cell biology 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about cell biology.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Cell biology revision resources
This page lists the understandings and skills expected for Topic 1 and links to the sub-topic pages which contain detailed revision notes, activities and past paper style questions. Great for revision.
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
What is the best definition of endosymbiosis?
Endosymbiosis is where a cell engulfs another cell and it continues to live inside the cell.
The engulfed cell provides something for the host cell, and gets something in return. Both cells benefit.
The image below was taken in 1825 and shows part of the cell cycle.
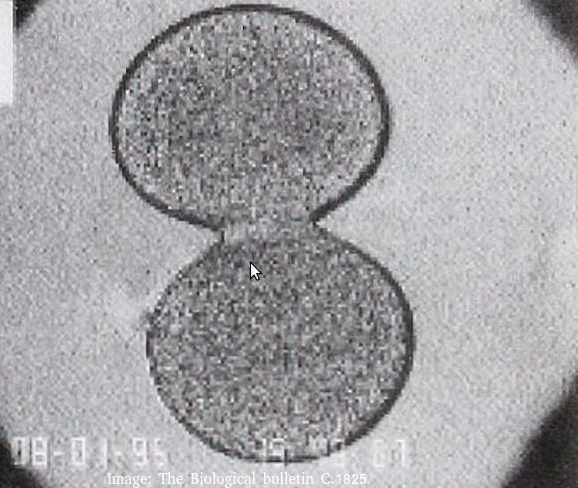
What type of cells is this and at which stage of the cell cycle?
Cytokinesis occurs after mitosis in plant and animal cells. The chromosomes are uncoiled.
Plant cells build a new cell wall which divides the cytoplasm.
Animal cells form a cleavage furrow (likes a wasps waist) as they don't have cell walls.
The microscope image shows cells in a tissue sample taken from a growth suspected of being cancerous.
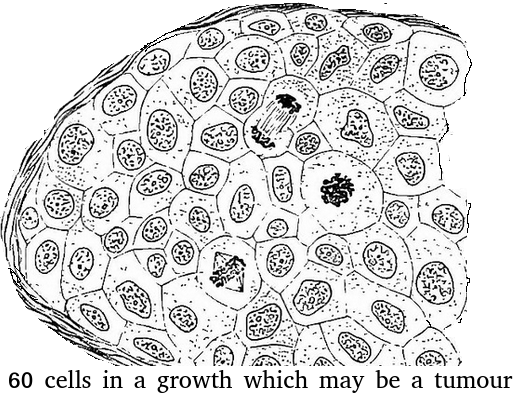
What is the best estimate of the mitotic index of this tissue?
Assume that there are exactly 60 cells (for simplicity).
Skill: Determination of a mitotic index from a micrograph
There are 3 cells in stages of mitosis.
So the mitotic index = 3 divided by 60 cells total.
Keeping it simple = 1 / 20 or 0.05
Sodium channels are made from a protein.
Where in the cell are sodium channel proteins found?
Sodium channel proteins are found spanning the plasma membrane. Their structure helps the function for facilitated diffusion in cells because they allow ions to pass cross the membrane.
If the protein was not a trans-membrane protein then it would not be able to transport ions across the membrane.
This box contains a lung waiting for a transplant operation.
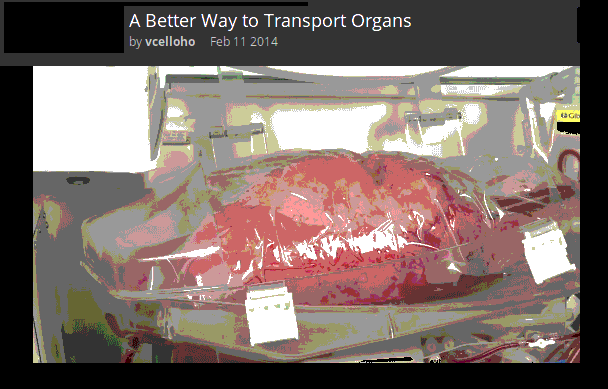
What is special about the solution inside the box which surrounds the tissue?
Tissues and organs must be kept in a solution with the same osmolarity as the cytoplasm of the cells to prevent osmosis. If they were kept in pure water, osmosis would carry water into the cells and they would burst, causing damage to the cells. If the solution was hypertonic, the tissue would lose water (and gain ions).
The four cells shown below have each been surrounded by a solution for 1 hour.
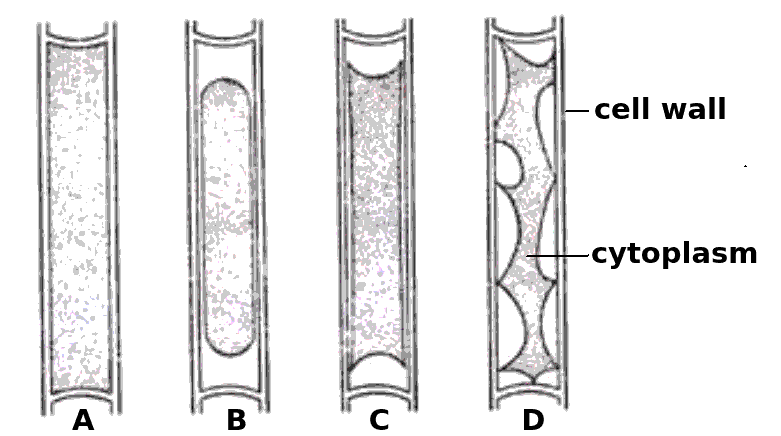
Which cells have been in a hypertonic solution ?
Cell A is swollen turgid, it is in a hypotonic solution or an isotonic solution.
The cells B, C and D show increasing signs of plasmolysis, and so they must be in hypertonic solutions.
Skill: Estimation of osmolarity in tissues by bathing samples in hypotonic and hypertonic solutions. (Practical 2)
Which of the following is true of peripheral proteins in cell membranes?
Membrane proteins are diverse in terms of structure, position in the membrane and function.
Peripheral proteins are attached to the membrane but found on its surface.
If you found a eukaryote cell in an electron microscope image, and it contained a lot of rER, Golgi apparatus and many darkly stained vesicles, what do you think the function of the cell is most likely to be?
(eg. goblet cells which make mucus (a protien) will contain lots of rER and vesicles of musus, and palisade mesophyll cells which do photosynthesis will contain lots of chloroplasts)
Why is it that prokaryotes can divide by the simple process of binary fission, but eukaryotes have to divide by the more complex process of mitosis?
To explain how the structure of prokaryotes allows them to divide by binary fission you could mention:
- Prokaryotes have a single chromosome, eukaryotes have multiple chromosomes
- Prokaryotes have no nuclear membrane, which eukaryotes have.
Stargarts disease, which causes loss of cells in the retina can be treated using a special type of human cell.
Which of the following is used because it is still able to differentiate?
Stem cells can differentiate and become specialised cells.
They often take on the features of the cells around them.
Rod cells, cone cells, and erythrocytes are specialised cells and cannot differentiate.
Cells are often stored in isotonic conditions because they can be damaged in other concentrations, hypertonic, or hypotonic. Which of the descriptions of hypertonic is the most accurate?
Hypertonic solutions have a higher concentration of solutes, and lower water potentials than cells.
The image below shows a eukaryotic cell.
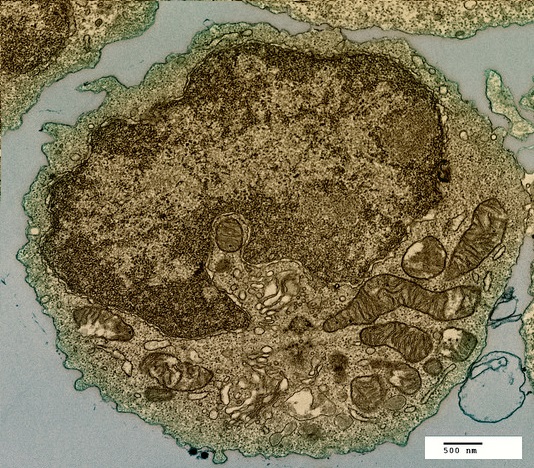
Which structure, visible in the image, could be used as evidence supporting endosymbiosis?
The mitochondria provide evidence supporting endosymbiosis because they have:
- a double membrane
- 70S ribosomes
- DNA
Which phrases most accurately describe a multicellular organism?
Comment: The multicellular condition allows for differentiation into cells of different types and also replacement of cells when injured or damaged.
Which is the correct order of SI units, beginning with the largest?
Comment: SI units always have a differential of 1000. The unit without the prefix is the standard SI unit (metre, m). B and D are clearly wrong, eliminate those answers first.
What is the approximate length of the bacterial cell in the image?

The scale bar is 1 µm and the bacterium is approximately 3 times the length of the scale bar.
The microphotograph is of stratified epithelium. Cells are produced by mitosis in the area marked 1 and eventually reach the surface to replace lost cells. Which biological processes does this represent?

The cells produced by mitosis differentiate into mature cells and replace the cells lost at the surface.
Which means of transport across a plasma membrane requires the molecule shown in the picture?

A mitotic index taken from this microphotograph only would not be regarded as valid. How can a valid count be made?

Which of the following are believed to be endosymbiotic structures involved in cell locomotion in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Flagellae are locomotory structures found in some Monera (bacteria), and some eukaryotic cells such as male gametes and Protoctista. Mitochondria are not found in prokaryotes. Pseudopodia are involved in locomotion but only in cells without an external wall. Fimbriae in bacteria allow for binding to a host or substrate, the same name is given to projections in the oviduct that aid movement of the ovum towards the uterus.
There are twenty complete cells in this microphotograph (with complete nuclear material). Estimate the number of complete cells in prophase of mitosis.

There are 3 complete cells in prophase (chromosomes visible in a nucleus..
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.

 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn