Topic 1: Cell biology 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about cell biology.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Cell biology revision resources
This page lists the understandings and skills expected for Topic 1 and links to the sub-topic pages which contain detailed revision notes, activities and past paper style questions. Great for revision.
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
The 64 codons of mRNA code for the same amino acids in almost all species. A rare exception is found in Paramecium where one of the "stop codons" actually codes for the amino acid glutamine.
What does this suggest about the origin of cells?
The 64 codons in the genetic code give rise to the same amino acids in nearly all organisms, There is very little variaion. If the genetic code had evolved several times in the history off life, there would be many differences.
Sodium channels are made from a protein.
Where in the cell are sodium channel proteins found?
Sodium channel proteins are found spanning the plasma membrane. Their structure helps the function for facilitated diffusion in cells because they allow ions to pass cross the membrane.
If the protein was not a trans-membrane protein then it would not be able to transport ions across the membrane.
The four cells shown below have each been surrounded by a solution for 1 hour.
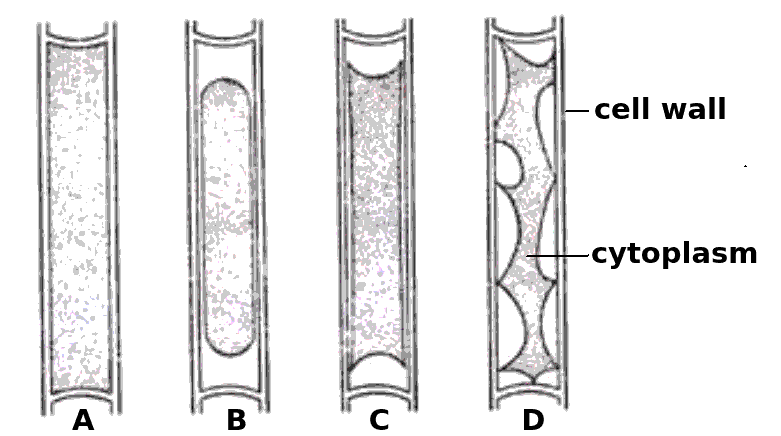
Which cells have been in a hypertonic solution ?
Cell A is swollen turgid, it is in a hypotonic solution or an isotonic solution.
The cells B, C and D show increasing signs of plasmolysis, and so they must be in hypertonic solutions.
Skill: Estimation of osmolarity in tissues by bathing samples in hypotonic and hypertonic solutions. (Practical 2)
The graph below shows the % change in mass of carrot parenchyma slices at different concentrations of sucrose.
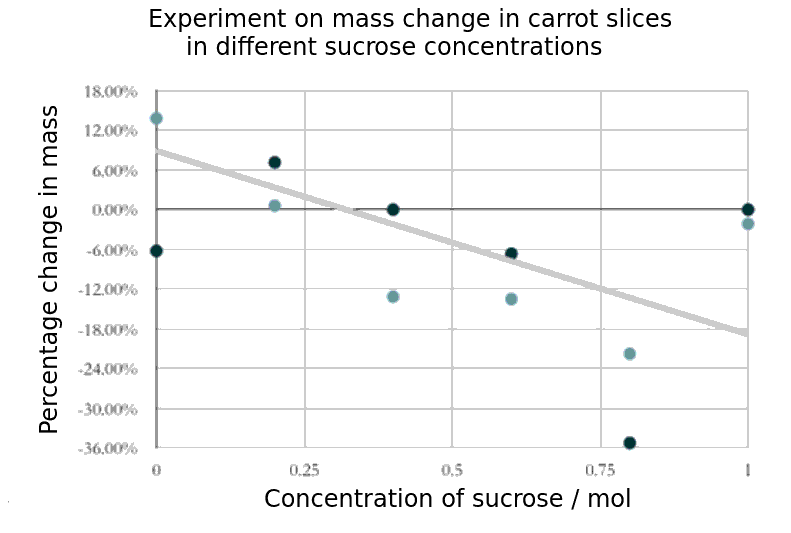
Which of the following is the best estimate of the molarity of the cytoplasm of these cells?
When a sample of cells show no change in mass, then the net movement of water by osmosis must be zero. This shows the concentration of the cytoplasm of the cells. In this graph it would be about 0.3 mol
What effect does reducing the amount of cholesterol in a cell membrane have on its properties?
Cholesterol is a component of animal cell membranes. Application: Cholesterol in mammalian membranes reduces membrane fluidity and permeability to some solutes.
What are the structures labelled X and Y likely to be in this electron microscope image?
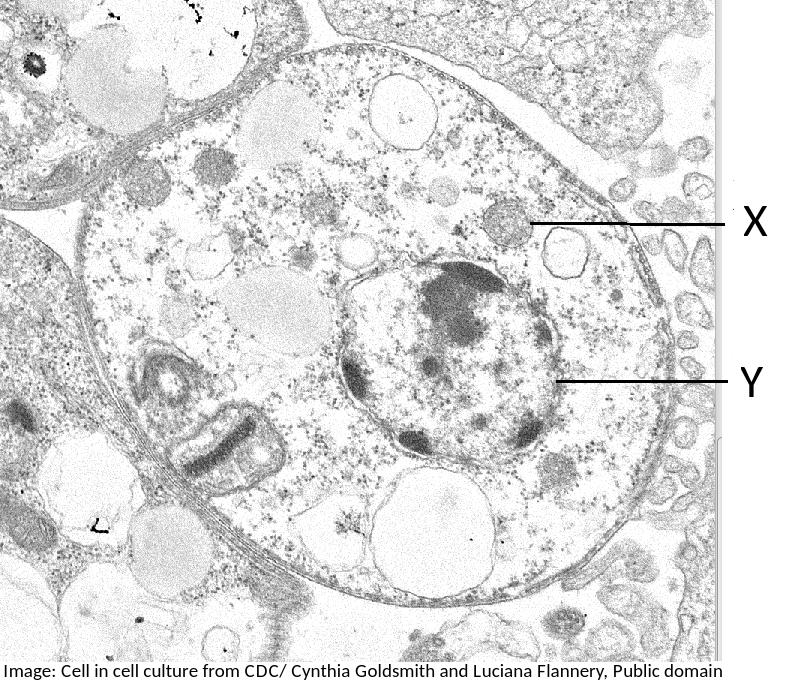
Students are expected to be able to identify organelles from microscope images of cells. The nucleus is distinctive because it is about 10µm in size, and it has black dots in it, chromatin, and sometimes one or more dark patches within the nuclear membrane. It also has a double membrane, not often easily visible.
Cell theory covers most, but not all cases.
Which one of these statements is an exception?
Exceptions to cell theory are : multinucleated striated muscle the giant single celled Acetabularia algae?
Also, organisms consisting of only one cell carry out all functions of life in that cell. e.g. Paramecium, Chlorella.
The blood cells below were imaged using an electron microscope.
The magnification is x3000 and the ruler measures the central cell as being 2 cm in diameter.
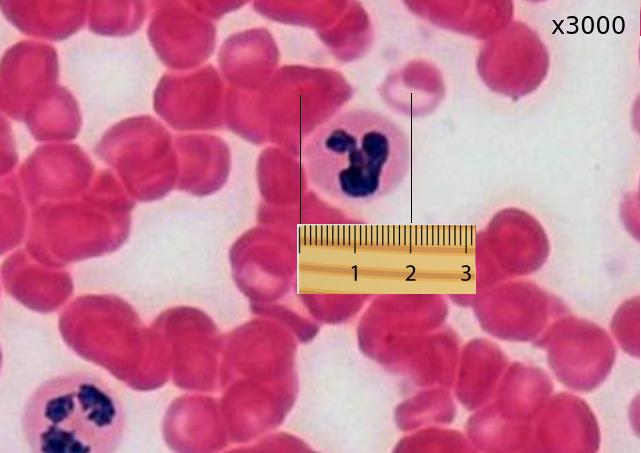
Estimate the actual size of this white blood cell.
Calculate specimen size using magnification?
First change the size measurement into µm units = 20000µm
Then divide by the magnification. 20000 / 3000 = 20 / 3 = 6.6 µm
Which of the structures listed below are involved in membrane transport?
Many transmembrane proteins are involved in transport of molecules across membranes. These can either provide a sort of molecular pore through which ions or molecules can pass (facilitated diffusion), or they can use ATP to actively move molecules, even against the concentration gradient (active transport).These are just two examples, transport can also occur by simple diffusion through the phospholipid bilayer, or by endocytosis.
Which is the best definition of a tissue?
Comment:Tissues may have one or several cell types and one or more functions
Which of the following could be used to distinguish a living from a non- living object
Comment: Inanimate objects can move, produce and utilise energy but the process of respiration is exclusive to living systems
Which organelles are found in large numbers in secretory cells in animals? I Vesicles II Golgi Body III Mitochondria IV Rough endoplasmic reticulum.

Secretory cells synthesise proteins for exocytosis so have large numbers of mitochondria to supply energy, RER to synthesise the proteins for packaging into vesicles by the Golgi Body.
The image shows a transverse section of a plant cell seen using an electron microscope.
What is the main function of the large organelle (A) seen in the cell?

The organelle shown is the nucleus, it stores the genetic information, DNA and is the location of DNA replication and Transcription.
The diagram is of a plasma membrane. Which label corresponds to the hydrophilic area of an amphipathic molecule?

Protein (5) has both hydrophilic and hydrophobic areas to act as an integral protein. The central channel is hydrophilic.
The microphotograph is of stratified epithelium. Cells are produced by mitosis in the area marked 1 and eventually reach the surface to replace lost cells. Which biological processes does this represent?

The cells produced by mitosis differentiate into mature cells and replace the cells lost at the surface.
What is the sequence of events that occur in a cell that is secreting a protein hormone?
1 Exocytosis
2 Vesicle formed by Golgi Body
3 Fusion of vesicle to plasma membrane
4 RER manufactures protein.
Ribosomes on the RER manufacture protein. This is packaged in vesicles by the Golgi Body and moves to the surface of the cell where the vesicle and plasma membrane fuse and exocytosis of the protein occurs.
What is the structure of the genetic material found in a mitochondrion?
Mitochondrial DNA is a single helical molecule, not associated with protein and circular in shape. The same as prokaryote nucleoid DNA.
Which of the following are believed to be endosymbiotic structures involved in cell locomotion in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Flagellae are locomotory structures found in some Monera (bacteria), and some eukaryotic cells such as male gametes and Protoctista. Mitochondria are not found in prokaryotes. Pseudopodia are involved in locomotion but only in cells without an external wall. Fimbriae in bacteria allow for binding to a host or substrate, the same name is given to projections in the oviduct that aid movement of the ovum towards the uterus.
In which ways is a plasma membrane fluid?
I The shape is flexible
II Proteins can move in and out of the membrane
III Proteins can move within the membrane
IV It can reseal a small puncture.
The membrane can reseal if slightly damaged and the shape is flexible. Proteins cannot move in and out of the membrane but can move within the membrane.
Which of the following is the best description of an organelle?
The "wrong" answers are correct statements but are distractors, not the best description.
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.

 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn